Sir2 plays a key role in cell fate determination upon SAPK activation
- PMID: 22245992
- PMCID: PMC3273896
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100419
Sir2 plays a key role in cell fate determination upon SAPK activation
Abstract
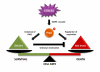
Although the benefit of sirtuin activation in age-related diseases is well-characterized, the benefit of sirtuin activation in acute diseases has been elusive. Here we discuss that, at least in yeast, Sir2 activation prevents programmed cell death induced by the sustained activation of the stress activated protein kinase (SAPK) Hog1, the yeast homologue of the p38 SAPK. Sir2 prevents ROS formation and maximize cell survival upon SAPK activation. The conserved function of Sir2 in age-related diseases and the conserved role of SAPKs open the possibility of a novel role for sirtuins in cell fate determination in eukaryotic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The implication of Sir2 in replicative aging and senescence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Mar;3(3):319-24. doi: 10.18632/aging.100299. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21415463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth phase-dependent roles of Sir2 in oxidative stress resistance and chronological lifespan in yeast.J Microbiol. 2014 Aug;52(8):652-8. doi: 10.1007/s12275-014-4173-2. Epub 2014 Jul 5. J Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24997552
-
Sir2 histone deacetylase prevents programmed cell death caused by sustained activation of the Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase.EMBO Rep. 2011 Sep 30;12(10):1062-8. doi: 10.1038/embor.2011.154. EMBO Rep. 2011. PMID: 21836634 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasomes, Sir2, and Hxk2 form an interconnected aging network that impinges on the AMPK/Snf1-regulated transcriptional repressor Mig1.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 28;11(1):e1004968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004968. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25629410 Free PMC article.
-
[The molecular mechanism of aging and longevity and the function of Sir2 proteins].Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2001 Nov;38(6):735-9. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11774709 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Metabolic respiration induces AMPK- and Ire1p-dependent activation of the p38-Type HOG MAPK pathway.PLoS Genet. 2014 Oct 30;10(10):e1004734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004734. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25356552 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress in genetics of aging, senescence and longevity: focusing on cancer-related genes.Oncotarget. 2012 Dec;3(12):1522-32. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.889. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 23455653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xenohormetic and anti-aging activity of secoiridoid polyphenols present in extra virgin olive oil: a new family of gerosuppressant agents.Cell Cycle. 2013 Feb 15;12(4):555-78. doi: 10.4161/cc.23756. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23370395 Free PMC article.
-
Hog1 acts in a Mec1-independent manner to counteract oxidative stress following telomerase inactivation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Commun Biol. 2024 Jun 22;7(1):761. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06464-3. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38909140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennedy BK, Gotta M, Sinclair DA, Mills K, McNabb DS, Murthy M, Pak SM, Laroche T, Gasser SM, Guarente L. Redistribution of silencing proteins from telomeres to the nucleolus is associated with extension of life span in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1997;89:381–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

