Effects and mechanism of downregulation of survivin expression by RNA interference on proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer cells
- PMID: 22246162
- PMCID: PMC3493107
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2012.755
Effects and mechanism of downregulation of survivin expression by RNA interference on proliferation and apoptosis of lung cancer cells
Abstract
The survivin protein, a member of the inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) family, has gained popularity as a therapeutic target for cancer due to its selective expression in tumor cells and its significant involvement in tumor cell viability. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of the survivin-small interfering RNA (siRNA) plasmid on survivin expression in the human lung cancer cell line, A549, and to observe its effects on apoptosis and proliferation of A549 cells. A549 human lung cancer cells were transfected with survivin-targeting siRNA. The downregulation of survivin expression was determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The proliferation of A549 cells was determined by MTT assay. The apoptotic rate and cell cycle distribution were analyzed by flow cytometry (FCM). Caspase-9 activity was also detected to study the apoptosis of lung cancer cells induced by siRNA against survivin. The sequence-specific siRNA efficiently and specifically downregulated the expression of survivin at both the mRNA and protein levels. Downregulation of survivin expression dramatically suppressed the proliferation of A549 cells and arrested the cells at the G (1)/G (0) phase. Caspase-9 activity was significantly increased in A549 cells transfected with siRNA against survivin. In this study, we found that survivin-specific siRNA can efficiently suppress the expression of survivin, increase apoptosis and inhibit A549 cell proliferation. Our findings further indicate the possibility that the antitumor effects of survivin-siRNA are mediated through the activation of caspase-9.
Figures
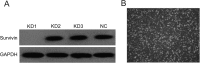

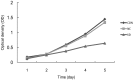
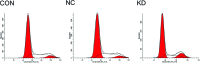
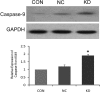
References
-
- Seve P, Dumontet C. Chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2005;5:73–88. - PubMed
-
- Lee MW, Kim DS, Min NY, Kim HT. Akt1 inhibition by RNA interference sensitizes human non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:2380–2384. - PubMed
-
- Dong AQ, Kong MJ, Ma ZY, Qian JF, Xu XH. Down-regulation of IGF-IR using small, interfering, hairpin RNA (siRNA) inhibits growth of human lung cancer cell line A549 in vitro and in nude mice. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31:500–507. - PubMed
-
- Ashihara E. RNA interference for cancer therapies. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2010;37:2033–2041. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima N, Huang CL, Liu D, Ueno M, Yokomise H. Intratumoral Wnt1 expression affects survivin gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 2010;37:687–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

