Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism
- PMID: 22246184
- PMCID: PMC3297996
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.489
Microvesicles released from microglia stimulate synaptic activity via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism
Abstract
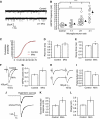
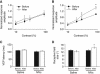
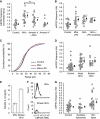
Microvesicles (MVs) released into the brain microenvironment are emerging as a novel way of cell-to-cell communication. We have recently shown that microglia, the immune cells of the brain, shed MVs upon activation but their possible role in microglia-to-neuron communication has never been explored. To investigate whether MVs affect neurotransmission, we analysed spontaneous release of glutamate in neurons exposed to MVs and found a dose-dependent increase in miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (mEPSC) frequency without changes in mEPSC amplitude. Paired-pulse recording analysis of evoked neurotransmission showed that MVs mainly act at the presynaptic site, by increasing release probability. In line with the enhancement of excitatory transmission in vitro, injection of MVs into the rat visual cortex caused an acute increase in the amplitude of field potentials evoked by visual stimuli. Stimulation of synaptic activity occurred via enhanced sphingolipid metabolism. Indeed, MVs promoted ceramide and sphingosine production in neurons, while the increase of excitatory transmission induced by MVs was prevented by pharmacological or genetic inhibition of sphingosine synthesis. These data identify microglia-derived MVs as a new mechanism by which microglia influence synaptic activity and highlight the involvement of neuronal sphingosine in this microglia-to-neuron signalling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
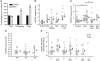
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511 - PubMed
-
- Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, Rak J (2008) Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 10: 619–624 - PubMed
-
- Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Rak J (2009) Microvesicles: messengers and mediators of tumor progression. Cell Cycle 8: 2014–2018 - PubMed
-
- Bacci A, Coco S, Pravettoni E, Schenk U, Armano S, Frassoni C, Verderio C, De Camilli P, Matteoli M (2001) Chronic blockade of glutamate receptors enhances presynaptic release and downregulates the interaction between synaptophysin-synaptobrevin-vesicle-associated membrane protein 2. J Neurosci 21: 6588–6596 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barenholz Y, Gibbes D, Litman BJ, Goll J, Thompson TE, Carlson RD (1977) A simple method for the preparation of homogeneous phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 16: 2806–2810 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

