Volumetric navigators for real-time motion correction in diffusion tensor imaging
- PMID: 22246720
- PMCID: PMC3330197
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.23314
Volumetric navigators for real-time motion correction in diffusion tensor imaging
Abstract
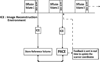
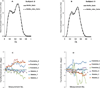
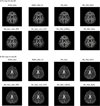
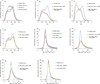
Prospective motion correction methods using an optical system, diffusion-weighted prospective acquisition correction, or a free induction decay navigator have recently been applied to correct for motion in diffusion tensor imaging. These methods have some limitations and drawbacks. This article describes a novel technique using a three-dimensional-echo planar imaging navigator, of which the contrast is independent of the b-value, to perform prospective motion correction in diffusion weighted images, without having to reacquire volumes during which motion occurred, unless motion exceeded some preset thresholds. Water phantom and human brain data were acquired using the standard and navigated diffusion sequences, and the mean and whole brain histogram of the fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity were analyzed. Our results show that adding the navigator does not influence the diffusion sequence. With head motion, the whole brain histogram-fractional anisotropy shows a shift toward lower anisotropy with a significant decrease in both the mean fractional anisotropy and the fractional anisotropy histogram peak location (P<0.01), whereas the whole brain histogram-mean diffusivity shows a shift toward higher diffusivity with a significant increase in the mean diffusivity (P<0.01), even after retrospective motion correction. These changes in the mean and the shape of the histograms are recovered substantially in the prospective motion corrected data acquired using the navigated sequence.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B. 1996;111(3):209–219. - PubMed
-
- Snook L, Paulson LA, Roy D, Phillips L, Beaulieu C. Diffusion tensor imaging of neurodevelopment in children and young adults. NeuroImage. 2005;26(4):1164–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21AA017410/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R21MH096559/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21EB008547/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA017410/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- G0700796/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 MH096559/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD071664/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB008547/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS05574/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HD071664/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

