Hypolipidemic agent Z-guggulsterone: metabolism interplays with induction of carboxylesterase and bile salt export pump
- PMID: 22246918
- PMCID: PMC3276476
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M014688
Hypolipidemic agent Z-guggulsterone: metabolism interplays with induction of carboxylesterase and bile salt export pump
Abstract
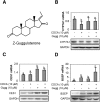
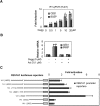
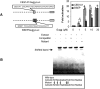
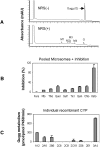
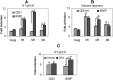
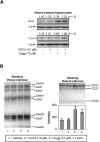
Z-Guggulsterone is a major ingredient in the Indian traditional hypolipidemic remedy guggul. A study in mice has established that its hypolipidemic effect involves the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), presumably by acting as an antagonist of this receptor. It is generally assumed that the antagonism leads to induction of cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1), the rate-limiting enzyme converting free cholesterol to bile acids. In this study, we tested whether Z-guggulsterone indeed induces human CYP7A1. In addition, the expression of cholesteryl ester hydrolase CES1 and bile salt export pump (BSEP) was monitored. Contrary to the general assumption, Z-guggulsterone did not induce CYP7A1. Instead, this phytosterol significantly induced CES1 and BSEP through transactivation. Z-Guggulsterone underwent metabolism by CYP3A4, and the metabolites greatly increased the induction potency on BSEP but not on CES1. BSEP induction favors cholesterol elimination, whereas CES1 involves both elimination and retention (probably when excessively induced). Interestingly, clinical trials reported the hypolipidemic response rates from 18% to 80% and showed that higher dosages actually increased VLDL cholesterol. Our findings predict that better hypolipidemic outcomes likely occur in individuals who have a relatively higher capacity of metabolizing Z-guggulsterone with moderate CES1 induction, a scenario possibly achieved by lowering the dosing regimens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The hypolipidemic agent guggulsterone regulates the expression of human bile salt export pump: dominance of transactivation over farsenoid X receptor-mediated antagonism.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Mar;320(3):1153-62. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.113837. Epub 2006 Nov 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17135343 Free PMC article.
-
Guggulsterone antagonizes farnesoid X receptor induction of bile salt export pump but activates pregnane X receptor to inhibit cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Apr 25;304(1):191-5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00551-5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003. PMID: 12705905
-
Guggulsterone is a farnesoid X receptor antagonist in coactivator association assays but acts to enhance transcription of bile salt export pump.J Biol Chem. 2003 Mar 21;278(12):10214-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209323200. Epub 2003 Jan 13. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12525500
-
Therapeutic effects of guggul and its constituent guggulsterone: cardiovascular benefits.Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007 Winter;25(4):375-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2007.00023.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2007. PMID: 18078436 Review.
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
Cited by
-
Gugulipid causes hypercholesterolemia leading to endothelial dysfunction, increased atherosclerosis, and premature death by ischemic heart disease in male mice.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 14;12(9):e0184280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184280. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28910310 Free PMC article.
-
Guggulsterone induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through intrinsic mitochondrial pathway.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 21;21(47):13277-87. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13277. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26715810 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related inducibility of carboxylesterases by the antiepileptic agent phenobarbital and implications in drug metabolism and lipid accumulation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 15;84(2):232-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22513142 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Product-Induced Modulation of Androstenone Metabolism in Porcine Hepatocytes.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 25;15(15):2199. doi: 10.3390/ani15152199. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804989 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of the pregnane X receptor during endoplasmic reticulum stress is achieved by down-regulating hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α and up-regulating liver-enriched inhibitory protein.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Apr;144(2):382-92. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfv008. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25616597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buemi M., Aloisi C., Fulvio F., Caccamo C., Cavallaro E., Crascì E., Criseo M., Corica F., Frisina N. 2005. Cardiorenal consequences of atherosclerosis and statins therapy: from the past to the future. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11: 3973–3984. - PubMed
-
- Wei E., Alam M., Sun F., Agellon L. B., Vance D. E., Lehner R. 2007. Apolipoprotein B and triacylglycerol secretion in human triacylglycerol hydrolase transgenic mice. J. Lipid Res. 48: 2597–2606. - PubMed
-
- Wei E., Ben Ali Y., Lyon J., Wang H., Nelson R., Dolinsky V. W., Dyck J. R., Mitchell G., Korbutt G. S., Lehner R. 2010. Loss of TGH/Ces3 in mice decreases blood lipids, improves glucose tolerance, and increases energy expenditure. Cell Metab. 11: 183–193. - PubMed
-
- Blais D. R., Lyn R. K., Joyce M. A., Rouleau Y., Steenbergen R., Barsby N., Zhu L. F., Pegoraro A. F., Stolow A., Tyrrell D. L., et al. 2010. Activity-based protein profiling identifies a host enzyme, carboxylesterase 1, which is differentially active during hepatitis C virus replication. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 25602–25612. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

