Secreted proteins as a fundamental source for biomarker discovery
- PMID: 22247067
- PMCID: PMC3517109
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201100346
Secreted proteins as a fundamental source for biomarker discovery
Abstract
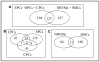
The proteins secreted by various cells (the secretomes) are a potential rich source of biomarkers as they reflect various states of the cells at real time and at given conditions. To have accessible, sufficient and reliable protein markers is desirable as they mark various stages of disease development and their presence/absence can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, risk stratification and therapeutic monitoring. As direct analysis of blood/plasma, a common and noninvasive patient screening method, can be difficult for candidate protein biomarker identification, the alternative/complementary approaches are required, one of them is the analysis of secretomes in cell conditioned media in vitro. As the proteins secreted by cells as a response to various stimuli are most likely secreted into blood/plasma, the identification and pre-selection of candidate protein biomarkers from cell secretomes with subsequent validation of their presence at higher levels in serum/plasma is a promising approach. In this review, we discuss the proteins secreted by three progenitor cell types (smooth muscle, endothelial and cardiac progenitor cells) and two adult cell types (neonatal rat ventrical myocytes and smooth muscle cells) which can be relevant to cardiovascular research and which have been recently published in the literature. We found, at least for secretome studies included in this review, that secretomes of progenitor and adult cells overlap by 48% but the secretomes are very distinct among progenitor cell themselves as well as between adult cells. In addition, we compared secreted proteins to protein identifications listed in the Human Plasma PeptideAtlas and in two reports with cardiovascular-related proteins and we performed the extensive literature search to find if any of these secreted proteins were identified in a biomarker study. As expected, many proteins have been identified as biomarkers in cancer but 18 proteins (out of 62) have been tested as biomarkers in cardiovascular diseases as well.
Copyright © 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Makridakis M, Vlahou A. Secretome proteomics for discovery of cancer biomarkers. J Proteomics. 2010;73:2291–2305. - PubMed
-
- Celis JE, Gromov P, Cabezon T, Moreira JM, et al. Proteomic characterization of the interstitial fluid perfusing the breast tumor microenvironment: a novel resource for biomarker and therapeutic target discovery. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004;3:327–344. - PubMed
-
- He J, Gornbein J, Shen D, Lu M, et al. Detection of breast cancer biomarkers in nipple aspirate fluid by SELDI-TOF and their identification by combined liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Int J Oncol. 2007;30:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

