Biochemical and mutational analyses of a multidomain cellulase/mannanase from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii
- PMID: 22247178
- PMCID: PMC3302618
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.06814-11
Biochemical and mutational analyses of a multidomain cellulase/mannanase from Caldicellulosiruptor bescii
Abstract
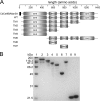
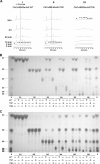
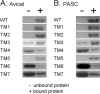
Thermophilic cellulases and hemicellulases are of significant interest to the biofuel industry due to their perceived advantages over their mesophilic counterparts. We describe here biochemical and mutational analyses of Caldicellulosiruptor bescii Cel9B/Man5A (CbCel9B/Man5A), a highly thermophilic enzyme. As one of the highly secreted proteins of C. bescii, the enzyme is likely to be critical to nutrient acquisition by the bacterium. CbCel9B/Man5A is a modular protein composed of three carbohydrate-binding modules flanked at the N terminus and the C terminus by a glycoside hydrolase family 9 (GH9) module and a GH5 module, respectively. Based on truncational analysis of the polypeptide, the cellulase and mannanase activities within CbCel9B/Man5A were assigned to the N- and C-terminal modules, respectively. CbCel9B/Man5A and its truncational mutants, in general, exhibited a pH optimum of ∼5.5 and a temperature optimum of 85°C. However, at this temperature, thermostability was very low. After 24 h of incubation at 75°C, the wild-type protein maintained 43% activity, whereas a truncated mutant, TM1, maintained 75% activity. The catalytic efficiency with phosphoric acid swollen cellulose as a substrate for the wild-type protein was 7.2 s(-1) ml/mg, and deleting the GH5 module led to a mutant (TM1) with a 2-fold increase in this kinetic parameter. Deletion of the GH9 module also increased the apparent k(cat) of the truncated mutant TM5 on several mannan-based substrates; however, a concomitant increase in the K(m) led to a decrease in the catalytic efficiencies on all substrates. These observations lead us to postulate that the two catalytic activities are coupled in the polypeptide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analyses of two thermophilic enzymes exhibiting both beta-1,4 mannosidic and beta-1,4 glucosidic cleavage activities from Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus.J Bacteriol. 2010 Aug;192(16):4111-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.00257-10. Epub 2010 Jun 18. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20562312 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biochemical analyses of CbCel9A/Cel48A, a highly secreted multi-modular cellulase by Caldicellulosiruptor bescii during growth on crystalline cellulose.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 16;8(12):e84172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084172. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24358340 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and biochemical analyses of the GH44 module of CbMan5B/Cel44A, a bifunctional enzyme from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Caldicellulosiruptor bescii.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Oct;78(19):7048-59. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02009-12. Epub 2012 Jul 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22843537 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the C-Terminal GH5 Domain from CbCel9B/Man5A as the First Glycoside Hydrolase with Thermal Activation Property from a Multimodular Bifunctional Enzyme.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 3;11(6):e0156802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156802. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27258548 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Cloning, Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a Family 5 Glycoside Hydrolase First Endo-Mannanase (RfGH5_7) from Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 v3.Mol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov;61(11):826-835. doi: 10.1007/s12033-019-00205-2. Mol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31435842
Cited by
-
Reassembly and co-crystallization of a family 9 processive endoglucanase from its component parts: structural and functional significance of the intermodular linker.PeerJ. 2015 Sep 15;3:e1126. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1126. eCollection 2015. PeerJ. 2015. PMID: 26401442 Free PMC article.
-
Thermophilic β-mannanases from bacteria: production, resources, structural features and bioengineering strategies.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 9;40(4):130. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03912-4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38460032 Review.
-
Caldicellulosiruptor bescii Adheres to Polysaccharides via a Type IV Pilin-Dependent Mechanism.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Apr 17;86(9):e00200-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00200-20. Print 2020 Apr 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32086304 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidation of a non-phenolic lignin model compound by two Irpex lacteus manganese peroxidases: evidence for implication of carboxylate and radicals.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017 Apr 21;10:103. doi: 10.1186/s13068-017-0787-z. eCollection 2017. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2017. PMID: 28439296 Free PMC article.
-
Thermostable enzymes and polysaccharides produced by thermophilic bacteria isolated from Bulgarian hot springs.Eng Life Sci. 2018 Jun 4;18(11):758-767. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201800022. eCollection 2018 Nov. Eng Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 32624870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai T, et al. 2001. Sequence of celQ and properties of CelQ, a component of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57:660–666 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

