A comprehensive dataset of genes with a loss-of-function mutant phenotype in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 22247268
- PMCID: PMC3291275
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.192393
A comprehensive dataset of genes with a loss-of-function mutant phenotype in Arabidopsis
Abstract
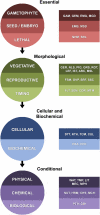
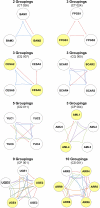
Despite the widespread use of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) as a model plant, a curated dataset of Arabidopsis genes with mutant phenotypes remains to be established. A preliminary list published nine years ago in Plant Physiology is outdated, and genome-wide phenotype information remains difficult to obtain. We describe here a comprehensive dataset of 2,400 genes with a loss-of-function mutant phenotype in Arabidopsis. Phenotype descriptions were gathered primarily from manual curation of the scientific literature. Genes were placed into prioritized groups (essential, morphological, cellular-biochemical, and conditional) based on the documented phenotypes of putative knockout alleles. Phenotype classes (e.g. vegetative, reproductive, and timing, for the morphological group) and subsets (e.g. flowering time, senescence, circadian rhythms, and miscellaneous, for the timing class) were also established. Gene identities were classified as confirmed (through molecular complementation or multiple alleles) or not confirmed. Relationships between mutant phenotype and protein function, genetic redundancy, protein connectivity, and subcellular protein localization were explored. A complementary dataset of 401 genes that exhibit a mutant phenotype only when disrupted in combination with a putative paralog was also compiled. The importance of these genes in confirming functional redundancy and enhancing the value of single gene datasets is discussed. With further input and curation from the Arabidopsis community, these datasets should help to address a variety of important biological questions, provide a foundation for exploring the relationship between genotype and phenotype in angiosperms, enhance the utility of Arabidopsis as a reference plant, and facilitate comparative studies with model genetic organisms.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of mitochondrial coenzyme a transporters from maize and Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2013 Jun;162(2):581-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.218081. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23590975 Free PMC article.
-
The Chloroplast Function Database II: a comprehensive collection of homozygous mutants and their phenotypic/genotypic traits for nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins.Plant Cell Physiol. 2013 Feb;54(2):e2. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs171. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23230006
-
Identification of nuclear genes encoding chloroplast-localized proteins required for embryo development in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2011 Apr;155(4):1678-89. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.168120. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21139083 Free PMC article.
-
A survey of dominant mutations in Arabidopsis thaliana.Trends Plant Sci. 2013 Feb;18(2):84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Trends Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 22995285 Review.
-
Genome-wide association studies in plants: the missing heritability is in the field.Genome Biol. 2011 Oct 28;12(10):232. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-232. Genome Biol. 2011. PMID: 22035733 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systems genetics approach to deciphering the effect of dosage variation on leaf morphology in Populus.Plant Cell. 2021 May 31;33(4):940-960. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaa016. Plant Cell. 2021. PMID: 33793772 Free PMC article.
-
A seed resource for screening functionally redundant genes and isolation of new mutants impaired in CO2 and ABA responses.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jan 7;70(2):641-651. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery363. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30346611 Free PMC article.
-
Plastid ribosome protein L5 is essential for post-globular embryo development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Reprod. 2022 Sep;35(3):189-204. doi: 10.1007/s00497-022-00440-9. Epub 2022 Mar 5. Plant Reprod. 2022. PMID: 35247095 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorophyll Fluorescence Video Imaging: A Versatile Tool for Identifying Factors Related to Photosynthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jan 30;9:55. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00055. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29472935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated Methods Enable Direct Computation on Phenotypic Descriptions for Novel Candidate Gene Prediction.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jan 10;10:1629. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01629. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 31998331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
-
- Becraft PW, Li K, Dey N, Asuncion-Crabb Y. (2002) The maize dek1 gene functions in embryonic pattern formation and cell fate specification. Development 129: 5217–5225 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

