Downregulation of SMG-1 in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma due to promoter hypermethylation correlates with improved survival
- PMID: 22247495
- PMCID: PMC4010255
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2058
Downregulation of SMG-1 in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma due to promoter hypermethylation correlates with improved survival
Abstract
Purpose: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is linked with a subset of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC). HPV-positive HNSCCs show a better prognosis than HPV-negative HNSCCs, which may be explained by sensitivity of the HPV-positive HNSCCs to ionizing radiation (IR). Although the molecular mechanism behind sensitivity to IR in HPV-positive HNSCCs is unresolved, DNA damage response (DDR) might be a significant determinant of IR sensitivity. An important player in the DDR, SMG-1 (suppressor with morphogenetic effect on genitalia), is a potential tumor suppressor and may therefore be deregulated in cancer. No studies have yet been conducted linking defects in SMG-1 expression with cancer. We investigated whether deregulation of SMG-1 could be responsible for defects in the DDR in oropharyngeal HNSCC.
Experimental design: Expression and promoter methylation status of SMG-1 were investigated in HNSCCs. To identify a functional link between HPV infection and SMG-1, we transfected the HPV-negative cells with an E6/E7 expression construct. SMG-1 short hairpin RNAs were expressed in HPV-negative cells to estimate survival upon IR.
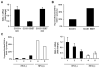
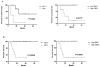
Results: Forced E6/E7 expression in HPV-negative cells resulted in SMG-1 promoter hypermethylation and decreased SMG-1 expression. Due to promoter hypermethylation, HPV-positive HNSCC cells and tumors express SMG-1 at lower levels than HPV-negative SCCs. Depletion of SMG-1 in HPV-negative HNSCC cells resulted in increased radiation sensitivity, whereas SMG-1 overexpression protected HPV-positive tumor cells from irradiation.
Conclusions: Levels of SMG-1 expression negatively correlated with HPV status in cancer cell lines and tumors. Diminished SMG-1 expression may contribute to the enhanced response to therapy exhibited by HPV-positive HNSCCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of human papilloma virus infection on the response of head and neck cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapy.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Feb 27;5(2):e1091. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.62. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24577089 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic patterns in head and neck cancers that contain or lack transcriptionally active human papillomavirus.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Jul 7;96(13):998-1006. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh183. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004. PMID: 15240783
-
Molecular genetic characterization of p53 mutated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells transformed with human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes.Int J Oncol. 2013 Aug;43(2):383-93. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1953. Epub 2013 May 24. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23708675 Free PMC article.
-
Biological basis for increased sensitivity to radiation therapy in HPV-positive head and neck cancers.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:696028. doi: 10.1155/2014/696028. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24804233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Nov;15(12):1319-31. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70471-1. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25439690
Cited by
-
New Concepts for Translational Head and Neck Oncology: Lessons from HPV-Related Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Front Oncol. 2012 Apr 11;2:36. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00036. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22655271 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant DNA Methylation Status and mRNA Expression Level of SMG1 Gene in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Case-Control Study.Cell J. 2022 Dec 1;24(12):757-763. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.8526. Cell J. 2022. PMID: 36527348 Free PMC article.
-
DGCR8/miR-106 Axis Enhances Radiosensitivity of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas by Downregulating RUNX3.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Dec 15;7:582097. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.582097. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33385002 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-585 acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting hSMG-1.Clin Transl Oncol. 2017 May;19(5):546-552. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1562-5. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Clin Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27743168
-
DNA Methylation Changes in Human Papillomavirus-Driven Head and Neck Cancers.Cells. 2020 May 31;9(6):1359. doi: 10.3390/cells9061359. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32486347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Denning G, Jamieson L, Maquat LE, Thompson EA, Fields AP. Cloning of a novel phosphatidylinositol kinase-related kinase: characterization of the human SMG-1 RNA surveillance protein. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(25):22709–14. - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L, Giulotto E, Lingner J. Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science. 2007;318(5851):798–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

