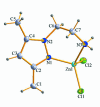
Dichlorido[2-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN)ethanamine-κN]zinc(II)
- PMID: 22247716
- PMCID: PMC3253618
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811044217
Dichlorido[2-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN)ethanamine-κN]zinc(II)
Abstract
The amine title complex, [ZnCl(2)(C(7)H(13)N(3))], resulted from imine hydrolysis in a Schiff base compound. The Zn metal atom has a distorted tetra-hedral geometry with the most significant deviation identified in the magnitude of the N-Zn-N angle. This deviation stems from the participation of the Zn and N atoms in a six-membered metallocyclic ring. The latter is in an approximate screw-boat conformation. Two strong N-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into ribbons propagating along the b-axis direction. The ribbons contain two second-order hydrogen-bonded motifs: a chain and a ring. The chain described by the graph set notation C(2) (2)(6) is formed by one hydrogen bond going in the forward direction (donor to acceptor) and the other in the backward direction (acceptor to donor). In the ring motif R(2) (2)(8), both hydrogen bonds propagate in the forward direction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
{1,2-Bis[(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN)meth-yl]benzene}-dichloridozinc(II).Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Dec 1;67(Pt 12):m1715-6. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811046368. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22199525 Free PMC article.
-
Dichlorido[2-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN(2))quinoline-κN]zinc.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 May 1;68(Pt 5):m571-2. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812014390. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22590087 Free PMC article.
-
cis-Dichlorido[2-(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN(2))ethanamine-κN]palladium(II) dichloro-methane monosolvate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Aug 1;68(Pt 8):m1103. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812032308. Epub 2012 Jul 21. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22904759 Free PMC article.
-
Dichlorido{2-morpholino-N-[1-(2-pyrid-yl)ethyl-idene]ethanamine-κN,N',N''}zinc(II).Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 Dec 11;67(Pt 1):m55. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810050671. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21522573 Free PMC article.
-
Dichlorido{2-[(2,6-dimethyl-phen-yl)imino-meth-yl]pyridine-κN,N'}zinc.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Mar 1;68(Pt 3):m311. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812006204. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22412452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
{1,2-Bis[(3,5-dimethyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl-κN)meth-yl]benzene}-dichloridozinc(II).Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Dec 1;67(Pt 12):m1715-6. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811046368. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 22199525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT-Plus Bruker-AXS Inc., Madison, WI, USA.
-
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Edgington, P. R., Kessler, M., Macrae, C. F., McCabe, P., Pearson, J. & Taylor, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 389–397. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous