Two lysines in the forkhead domain of foxp3 are key to T regulatory cell function
- PMID: 22247766
- PMCID: PMC3256141
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029035
Two lysines in the forkhead domain of foxp3 are key to T regulatory cell function
Abstract
Background: The forkhead box transcription factor, Foxp3, is master regulator of the development and function of CD4+CD25+ T regulatory (Treg) cells that limit autoimmunity and maintain immune homeostasis. The carboxyl-terminal forkhead (FKH) domain is required for the nuclear localization and DNA binding of Foxp3. We assessed how individual FKH lysines contribute to the functions of Foxp3 in Treg cells.
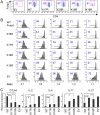
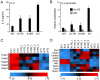
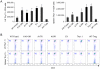
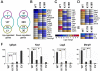
Methodology/principal findings: We found that mutation of FKH lysines at position 382 (K17) and at position 393 (K18) impaired Foxp3 DNA binding and inhibited Treg suppressive function in vivo and in vitro. These lysine mutations did not affect the level of expression of Foxp3 but inhibited IL-2 promoter remodeling and had important and differing effects on Treg-associated gene expression.
Conclusions/significance: These data point to complex effects of post-translational modifications at individual lysines within the Foxp3 FKH domain that affect Treg function. Modulation of these events using small molecule inhibitors may allow regulation of Foxp3+ Treg function clinically.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Feuerer M, Hill JA, Mathis D, Benoist C. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: differentiation, specification, subphenotypes. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:689–695. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–1061. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Rasmussen JP, Williams LM, Dooley JL, Farr AG, et al. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity. 2005;22:329–341. - PubMed
-
- Khattri R, Cox T, Yasayko SA, Ramsdell F. An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:337–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

