Potential key bases of ribosomal RNA to kingdom-specific spectra of antibiotic susceptibility and the possible archaeal origin of eukaryotes
- PMID: 22247777
- PMCID: PMC3256160
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029468
Potential key bases of ribosomal RNA to kingdom-specific spectra of antibiotic susceptibility and the possible archaeal origin of eukaryotes
Abstract
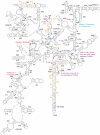
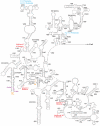
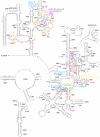
In support of the hypothesis of the endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotes, much evidence has been found to support the idea that some organelles of eukaryotic cells originated from bacterial ancestors. Less attention has been paid to the identity of the host cell, although some biochemical and molecular genetic properties shared by archaea and eukaryotes have been documented. Through comparing 507 taxa of 16S-18S rDNA and 347 taxa of 23S-28S rDNA, we found that archaea and eukaryotes share twenty-six nucleotides signatures in ribosomal DNA. These signatures exist in all living eukaryotic organisms, whether protist, green plant, fungus, or animal. This evidence explicitly supports the archaeal origin of eukaryotes. In the ribosomal RNA, besides A2058 in Escherichia coli vs. G2400 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, there still exist other twenties of sites, in which the bases are kingdom-specific. Some of these sites concentrate in the peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) of the 23S-28S rRNA. The results suggest potential key sites to explain the kingdom-specific spectra of drug resistance of ribosomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydroxylated histidine of human ribosomal protein uL2 is involved in maintaining the local structure of 28S rRNA in the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center.FEBS J. 2015 Apr;282(8):1554-66. doi: 10.1111/febs.13241. Epub 2015 Mar 5. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25702831
-
Rare ribosomal RNA sequences from archaea stabilize the bacterial ribosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 28;51(4):1880-1894. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1273. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36660825 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation from guanine to adenine in 25S rRNA at the position equivalent to E. coli A2058 does not confer erythromycin sensitivity in Sacchromyces cerevisae.RNA. 2008 Mar;14(3):460-4. doi: 10.1261/rna.786408. Epub 2008 Jan 24. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18218702 Free PMC article.
-
Intermolecular base-paired interaction between complementary sequences present near the 3' ends of 5S rRNA and 18S (16S) rRNA might be involved in the reversible association of ribosomal subunits.Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1913-29. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1913. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979. PMID: 94160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When stable RNA becomes unstable: the degradation of ribosomes in bacteria and beyond.Biol Chem. 2013 Jul;394(7):845-55. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0133. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23612597 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptional profiling of tildipirosin-resistant and sensitive Haemophilus parasuis.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 8;7(1):7517. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07972-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28790420 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular symplesiomorphies shared by the stem groups of metazoan evolution: can sites as few as 1% have a significant impact on recognizing the phylogenetic position of myzostomida?J Mol Evol. 2014 Aug;79(1-2):63-74. doi: 10.1007/s00239-014-9635-y. Epub 2014 Aug 17. J Mol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25128981
-
Evolution of replication machines.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 May-Jun;51(3):135-49. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1125845. Epub 2015 Dec 20. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27160337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant ribosomes as a score to fathom the melody of 2'-O-methylation across evolution.RNA Biol. 2024 Jan;21(1):70-81. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2024.2417152. Epub 2024 Nov 7. RNA Biol. 2024. PMID: 39508203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Arabidopsis 2'-O-Ribose-Methylation and Pseudouridylation Landscape of rRNA in Comparison to Human and Yeast.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 26;12:684626. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.684626. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34381476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Margulis L. Origin of Eukaryotic Cells. New Haven: Yale University Press; 1970.
-
- Deusch O, Landan G, Roettger M, Gruenheit N, Kowallik KV, et al. Genes of Cyanobacterial Origin in Plant Nuclear Genomes Point to a Heterocyst-Forming Plastid Ancestor. Mol Biol Evol. 2008;25:748–761. - PubMed
-
- Atteia A, Adrait A, Brugière S, Tardif M, Lis RV, et al. A Proteomic Survey of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Mitochondria Sheds New Light on the Metabolic Plasticity of the Organelle and on the Nature of the α-Proteobacterial Mitochondrial Ancestor. Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26:1533–1548. - PubMed
-
- Pennisi E. Evolutionary biology. The birth of the nucleus. Science. 2004;305:766–768. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

