Biological activities and medicinal properties of Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp
- PMID: 22247887
- PMCID: PMC3255353
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-4040.90874
Biological activities and medicinal properties of Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp
Abstract
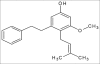
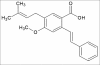
Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp. (Sanskrit: Adhaki, Hindi: Arhar, English: Pigeon pea, Bengali: Tur) (family: Fabaceae) is the most important grain legume crop of rain-fed agriculture in semi-arid tropics. It is both a food crop and a cover/forage crop with high levels of proteins and important amino acids like methionine, lysine and tryptophan. During the last few decades extensive studies have been carried out regarding the chemistry of C. cajan and considerable progress has been achieved regarding its biological activities and medicinal applications. This review article gives an overview on the biological activities of the compounds isolated, pharmacological actions and clinical studies of C. cajan extracts apart from its general details.
Keywords: Arhar; Cajanus cajan; biological and medicinal properties; fabaceae; pigeon pea.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









Similar articles
-
Revisiting the Nutritional, Chemical and Biological Potential of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.Molecules. 2022 Oct 13;27(20):6877. doi: 10.3390/molecules27206877. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HPLC-FRAP methodology and biological activities of different stem bark extracts of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021 Jan 5;192:113678. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113678. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021. PMID: 33120308
-
The Cholesterol-Modulating Effect of Methanol Extract of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) Leaves on Regulating LDLR and PCSK9 Expression in HepG2 Cells.Molecules. 2019 Jan 30;24(3):493. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030493. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30704067 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Diversity of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan L. Millsp.) Endosymbionts in India and Selection of Potential Strains for Use as Agricultural Inoculants.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Sep 7;12:680981. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.680981. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34557206 Free PMC article.
-
Progress of tissue culture and genetic transformation research in pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.].Plant Cell Rep. 2010 Oct;29(10):1079-95. doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0899-4. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Plant Cell Rep. 2010. PMID: 20652570 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Phytochemicals and Anti-Cancer Potential of the Members of Fabaceae Family: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2022 Jun 16;27(12):3863. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123863. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pinosylvin: A Multifunctional Stilbenoid with Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Potential.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 18;47(3):204. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030204. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification of miRNAs and lncRNAs in Cajanus cajan.BMC Genomics. 2017 Nov 15;18(1):878. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4232-2. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29141604 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Cajanus cajan Leaf Extracts for Nutraceutical Applications.Molecules. 2025 Apr 15;30(8):1773. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081773. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333766 Free PMC article.
-
Stilbenoids and Flavonoids from Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. and Their α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities.Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3779. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093779. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pal D, Sarkar A, Gain S, Jana S, Mandal S. CNS depressant activities of Coccos nucifera in mice. Acta Pol Pharm. 2011;68:249–54. - PubMed
-
- Pal DK, Mandal M, Senthilkumar GP, Padhiari A. Antibacterial activity of Cuscuta reflexa stem and Corchorus olitorius seed. Fitoterapia. 2006;77:589–91. - PubMed
-
- Pal DK, Pahari SK, Pathak AK. Evaluation of CNS activities of aerial parts of Jasminum multiflorum Andr. Asian J Chem. 2007;19:4452–8.
-
- Pal DK, Sannigrahi S, Mazumder UK. Analgesic and anticonvulsant effects of saponin isolated from the leaves of Clerodendrum infortunatum Linn. In mice. Indian J Exp Biol. 2009;47:743–7. - PubMed
-
- Pal DK, Sahoo M, Mishra A. Analgesic and anticonvulsant effects of saponin isolated from the stems of Opuntia vulgaris Mill in mice. Euro Bull Drug Res. 2005;13:91–7.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
