Prolonged oral cannabinoid administration prevents neuroinflammation, lowers β-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in Tg APP 2576 mice
- PMID: 22248049
- PMCID: PMC3292807
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-8
Prolonged oral cannabinoid administration prevents neuroinflammation, lowers β-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in Tg APP 2576 mice
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain shows an ongoing inflammatory condition and non-steroidal anti-inflammatories diminish the risk of suffering the neurologic disease. Cannabinoids are neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory agents with therapeutic potential.
Methods: We have studied the effects of prolonged oral administration of transgenic amyloid precursor protein (APP) mice with two pharmacologically different cannabinoids (WIN 55,212-2 and JWH-133, 0.2 mg/kg/day in the drinking water during 4 months) on inflammatory and cognitive parameters, and on ¹⁸F-fluoro-deoxyglucose (¹⁸FDG) uptake by positron emission tomography (PET).
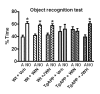
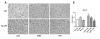
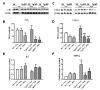
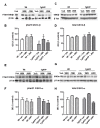
Results: Novel object recognition was significantly reduced in 11 month old Tg APP mice and 4 month administration of JWH was able to normalize this cognitive deficit, although WIN was ineffective. Wild type mice cognitive performance was unaltered by cannabinoid administration. Tg APP mice showed decreased ¹⁸FDG uptake in hippocampus and cortical regions, which was counteracted by oral JWH treatment. Hippocampal GFAP immunoreactivity and cortical protein expression was unaffected by genotype or treatment. In contrast, the density of Iba1 positive microglia was increased in Tg APP mice, and normalized following JWH chronic treatment. Both cannabinoids were effective at reducing the enhancement of COX-2 protein levels and TNF-α mRNA expression found in the AD model. Increased cortical β-amyloid (Aβ) levels were significantly reduced in the mouse model by both cannabinoids. Noteworthy both cannabinoids enhanced Aβ transport across choroid plexus cells in vitro.
Conclusions: In summary we have shown that chronically administered cannabinoid showed marked beneficial effects concomitant with inflammation reduction and increased Aβ clearance.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Microglial cannabinoid receptor type II stimulation improves cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease mice by controlling astrocyte activation.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Nov 26;15(11):858. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07249-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39587077 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil prevents neuroinflammation, lowers beta-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Aug 1;250:230-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.05.017. Epub 2013 May 16. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23685322
-
Dihydromyricetin inhibits microglial activation and neuroinflammation by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Dec;24(12):1207-1218. doi: 10.1111/cns.12983. Epub 2018 Jun 4. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29869390 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease; taking the edge off with cannabinoids?Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(5):655-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707446. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17828287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracking neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: the role of positron emission tomography imaging.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jul 8;11:120. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-120. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25005532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endocannabinoids in nervous system health and disease: the big picture in a nutshell.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;367(1607):3193-200. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0313. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108539 Free PMC article.
-
High-protein and low-calorie diets improved the anti-aging Klotho protein in the rats' brain: the toxic role of high-fat diet.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Oct 15;17:86. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00508-1. eCollection 2020. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33072166 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids in Neurology - Position paper from Scientific Departments from Brazilian Academy of Neurology.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2021 Apr;79(4):354-369. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2020-0432. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2021. PMID: 34133518 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoids in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Stroke/Brain Trauma: From Preclinical Models to Clinical Applications.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Oct;12(4):793-806. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0381-7. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 26260390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oridonin ameliorates neuropathological changes and behavioural deficits in a mouse model of cerebral amyloidosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Dec;17(12):1566-76. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12124. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24034629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Giffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O'Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. doi: 10.1016/S0197-4580(00)00124-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McGeer PL, Schulzer M, McGeer EG. Arthritis and anti-inflammatory agents as possible protective factors for Alzheimer's disease: A review of 17 epidemiologic studies. Neurology. 1997;47:425–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

