Delivering stepped care: an analysis of implementation in routine practice
- PMID: 22248385
- PMCID: PMC3283464
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-5908-7-3
Delivering stepped care: an analysis of implementation in routine practice
Abstract
Background: In the United Kingdom, clinical guidelines recommend that services for depression and anxiety should be structured around a stepped care model, where patients receive treatment at different 'steps,' with the intensity of treatment (i.e., the amount and type) increasing at each step if they fail to benefit at previous steps. There are very limited data available on the implementation of this model, particularly on the intensity of psychological treatment at each step. Our objective was to describe patient pathways through stepped care services and the impact of this on patient flow and management.
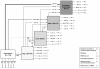
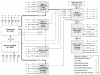
Methods: We recorded service design features of four National Health Service sites implementing stepped care (e.g., the types of treatments available and their links with other treatments), together with the actual treatments received by individual patients and their transitions between different treatment steps. We computed the proportions of patients accessing, receiving, and transiting between the various steps and mapped these proportions visually to illustrate patient movement.
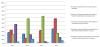
Results: We collected throughput data on 7,698 patients referred. Patient pathways were highly complex and very variable within and between sites. The ratio of low (e.g., self-help) to high-intensity (e.g., cognitive behaviour therapy) treatments delivered varied between sites from 22:1, through 2.1:1, 1.4:1 to 0.5:1. The numbers of patients allocated directly to high-intensity treatment varied from 3% to 45%. Rates of stepping up from low-intensity treatment to high-intensity treatment were less than 10%.
Conclusions: When services attempt to implement the recommendation for stepped care in the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence guidelines, there were significant differences in implementation and consequent high levels of variation in patient pathways. Evaluations driven by the principles of implementation science (such as targeted planning, defined implementation strategies, and clear activity specification around service organisation) are required to improve evidence on the most effective, efficient, and acceptable stepped care systems.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stepped care for depression in primary care: what should be offered and how?Med J Aust. 2010 Jun 7;192(S11):S36-9. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.2010.tb03691.x. Med J Aust. 2010. PMID: 20528706 Clinical Trial.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
-
Stepped care for depression and anxiety in visually impaired older adults: multicentre randomised controlled trial.BMJ. 2015 Nov 23;351:h6127. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h6127. BMJ. 2015. PMID: 26597263 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Stepped care targeting psychological distress in head and neck and lung cancer patients: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Cancer. 2012 May 10;12:173. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-173. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22574757 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Stepped-care treatment of anxiety and depression in older adults: A narrative review.Aust J Rural Health. 2019 Aug;27(4):275-280. doi: 10.1111/ajr.12524. Aust J Rural Health. 2019. PMID: 31429140 Review.
Cited by
-
What Would Digital Early Intervention for Bipolar Disorder Look Like? Theoretical and Translational Considerations for Future Therapies.Front Psychiatry. 2019 Aug 23;10:599. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00599. eCollection 2019. Front Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31507467 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing guidelines for depression on antidepressant prescribing in general practice: a quasi-experimental evaluation.BMC Fam Pract. 2014 Feb 19;15:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-15-35. BMC Fam Pract. 2014. PMID: 24552140 Free PMC article.
-
Rising tide: Responding to the mental health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.Depress Anxiety. 2020 Jun;37(6):505-509. doi: 10.1002/da.23058. Depress Anxiety. 2020. PMID: 32421214 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Distributive Leadership Within an Emerging Network of Integrated Youth Health Centres: A Case Study of Foundry.Int J Integr Care. 2020 Dec 1;20(4):19. doi: 10.5334/ijic.4709. Int J Integr Care. 2020. PMID: 33335460 Free PMC article.
-
Scoping review of stepped care interventions for mental health and substance use service delivery to youth and young adults.Early Interv Psychiatry. 2022 Apr;16(4):327-341. doi: 10.1111/eip.13180. Epub 2021 May 21. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34018335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grol R, Wensing M, Eccles M. Improving Patient Care. The Implementation of Change in Clinical Practice. London: Elsevier; 2005.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Depression: the treatment and management of depression in adults (update) CG90. London. 2009.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Depression in Adults with a Chronic Physical Health Problem: treatment and management CG91. London. 2009.
-
- Haaga D. Introduction to the special section on stepped care models in psychology. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2000;68:547–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical