HCV infection induces a unique hepatic innate immune response associated with robust production of type III interferons
- PMID: 22248663
- PMCID: PMC3435150
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.055
HCV infection induces a unique hepatic innate immune response associated with robust production of type III interferons
Abstract
Background & aims: Polymorphisms in the IL28B gene have been associated with clearance of hepatitis C virus (HCV), indicating a role for type III interferons (IFNs) in HCV infection. Little is known about the function of type III IFNs in intrinsic antiviral innate immunity.
Methods: We used in vivo and in vitro models to characterize the role of the type III IFNs in HCV infection and analyzed gene expression in liver biopsy samples from HCV-infected chimpanzees and patients. Messenger RNA and protein expression were studied in HCV-infected hepatoma cell lines and primary human hepatocytes.
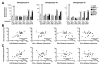
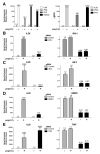
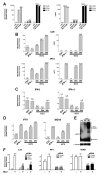
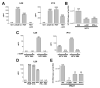
Results: HCV infection of primary human hepatocytes induced production of chemokines and type III IFNs, including interleukin (IL)-28, and led to expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs). Chimpanzees infected with HCV showed rapid induction of hepatic type III IFN, associated with up-regulation of ISGs and minimal induction of type I IFNs. In liver biopsy specimens from HCV-infected patients, hepatic expression of IL-28 correlated with levels of ISGs but not of type I IFNs. HCV infection produced extensive changes with gene expression in addition to ISGs in primary human hepatocytes. The induction of type III IFNs is regulated by IFN regulatory factor 3 and nuclear factor κB. Type III IFNs up-regulate ISGs with a different kinetic profile than type 1 IFNs and induce a distinct set of genes, which might account for their functional differences.
Conclusions: HCV infection results predominantly in induction of type III IFNs in livers of humans and chimpanzees; the level of induction correlates with hepatic levels of ISGs. These findings might account for the association among IL-28, level of ISGs, and recovery from HCV infection and provide a therapeutic strategy for patients who do not respond to IFN therapy.
Copyright © 2012 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
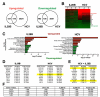

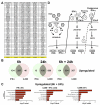
References
-
- Onomoto K, Onoguchi K, Takahasi K, et al. Type I interferon production induced by RIG-I-like receptors. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010;30:875–881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

