SFRP1 promoter methylation and expression in human trabecular meshwork cells
- PMID: 22248913
- PMCID: PMC6993145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2012.01.003
SFRP1 promoter methylation and expression in human trabecular meshwork cells
Abstract
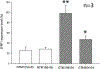
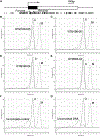
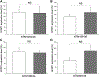
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness worldwide. In primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) patients, impaired trabecular meshwork (TM) function results in elevated intraocular pressure (IOP), which is the primary risk factor of developing optic neuropathy. Our previous studies showed that Wnt signaling pathway components are expressed in the human TM (HTM), and the Wnt inhibitor, secreted frizzled-related protein 1 (SFRP1) is elevated in the glaucomatous TM (GTM). Elevated SFRP1 increased IOP in mice eyes and in perfusion cultured anterior segments of the human eye. However, the cause of elevated SFRP1 in the GTM remains unknown. Promoter methylation plays a key role in regulating SFRP1 expression in certain cancer cells. In light of this, we studied whether promoter methylation is also involved in SFRP1 differential expression in the TM. Two normal TM (NTM) and two GTM cell strains were cultured for an additional 7 days after they were confluent. RNA and genomic DNA (gDNA) were isolated simultaneously to compare SFRP1 expression levels by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and to determine SFRP1 promoter methylation status by bisulfite conversion and methylation-sensitive high resolution melting analysis (MS-HRM). To study whether DNA methylation inhibitors affect SFRP1 expression in TM cells, the four TM cell strains were treated with or without 2 μM 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (AZA-dC) for 4 days. RNA was isolated to compare SFRP1 expression by qPCR. In addition, a human cancer cell line, NCI-H460, was used as a positive control. We found that the two GTM cell strains had significantly higher expression levels of SFRP1 than the two NTM cell strains. However, the SFRP1 promoter of all four TM cell strains was unmethylated. In addition, AZA-dC treatment did not affect SFRP1 expression in any of the TM cell strains (n = 3, p > 0.05). In contrast, the hypermethylated SFRP1 promoter of NCI-H460 cells was partially demethylated by the same treatment. AZA-dC treatment also elevated SFRP1 expression by approximately two fold in NCI-H460 cells (n = 3, p < 0.01). Our data suggest that the differential expression of SFRP1 in HTM cells is not due to differential promoter methylation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
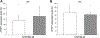
References
-
- The AGIS Investigators, 2000. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 7. The relationship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. Am. J. Ophthalmol 130, 429–440. - PubMed
-
- Baylin SB, Ohm JE, 2006. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer – a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 107–116. - PubMed
-
- Bovolenta P, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Cisneros E, Lopez-Rios J, 2008. Beyond Wnt inhibition: new functions of secreted frizzled-related proteins in development and disease. J. Cell. Sci 121, 737–746. - PubMed
-
- Fleenor DL, Shepard AR, Hellberg PE, Jacobson N, Pang IH, Clark AF, 2006. TGFbeta2-induced changes in human trabecular meshwork: implications for intraocular pressure. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci 47, 226–234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

