Epigenetic regulation of genomic integrity
- PMID: 22249206
- PMCID: PMC3982914
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-011-0358-1
Epigenetic regulation of genomic integrity
Abstract
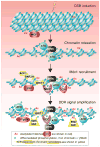
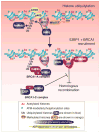
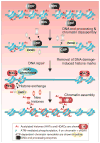
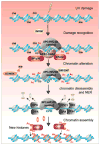
Inefficient and inaccurate repair of DNA damage is the principal cause of DNA mutations, chromosomal aberrations, and carcinogenesis. Numerous multiple-step DNA repair pathways exist whose deployment depends on the nature of the DNA lesion. Common to all eukaryotic DNA repair pathways is the need to unravel the compacted chromatin structure to facilitate access of the repair machinery to the DNA and restoration of the original chromatin state afterward. Accordingly, our cells utilize a plethora of coordinated mechanisms to locally open up the chromatin structure to reveal the underlying DNA sequence and to orchestrate the efficient and accurate repair of DNA lesions. Here we review changes to the chromatin structure that are intrinsic to the DNA damage response and the available mechanistic insight into how these chromatin changes facilitate distinct stages of the DNA damage repair pathways to maintain genomic stability.
Figures

References
-
- Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Bernal JA, Venkitaraman AR. HP1-[bgr] mobilization promotes chromatin changes that initiate the DNA damage response. Nature. 2008;453:682–686. - PubMed
-
- Ayoub N, Jeyasekharan AD, Venkitaraman AR. Mobilization and recruitment of HP1β: a bimodal response to DNA breakage. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:2946–2951. - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB. DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature. 2003;421:499–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

