Hindbrain leptin and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor signaling interact to suppress food intake in an additive manner
- PMID: 22249232
- PMCID: PMC3335926
- DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2011.265
Hindbrain leptin and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor signaling interact to suppress food intake in an additive manner
Abstract
Background: The physiological control of feeding behavior involves modulation of the intake inhibitory effects of gastrointestinal satiation signaling via endogenous hindbrain leptin receptor (LepR) and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) activation.
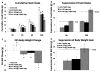
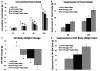
Design and results: Using a variety of dose-combinations of hindbrain delivered (4th intracerebroventricular; i.c.v.) leptin and the GLP-1R agonist exendin-4, experiments demonstrate that hindbrain LepR and GLP-1R signaling interact to control food intake and body weight in an additive manner. In addition, the maximum intake suppressive response that could be achieved by 4th i.c.v. leptin alone in non-obese rats (∼33%) was shown to be further suppressed when exendin-4 was co-administered. Importantly, it was determined that the interaction between hindbrain LepR signaling and GLP-1R signaling is relevant to endogenous food intake control, as hindbrain GLP-1R blockade by the selective antagonist exendin-(9-39) attenuated the intake inhibitory effects of hindbrain leptin delivery.
Conclusions: Collectively, the findings reported here show that hindbrain LepR and GLP-1R activation interact in at least an additive manner to control food intake and body weight. As evidence is accumulating that combination pharmacotherapies offer greater sustained food intake and body weight suppression in obese individuals when compared with mono-drug therapies or lifestyle modifications alone, these findings highlight the need for further examination of combined central nervous system GLP-1R and LepR signaling as a potential drug target for obesity treatment.
Figures

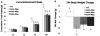
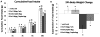
References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity: Data and Statistics. 2009.
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6):2087–102. - PubMed
-
- Wadden TA, Butryn ML, Wilson C. Lifestyle modification for the management of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6):2226–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

