Cutaneous papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins associate with MAML1 to repress transactivation and NOTCH signaling
- PMID: 22249263
- PMCID: PMC3330202
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.589
Cutaneous papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins associate with MAML1 to repress transactivation and NOTCH signaling
Abstract
Papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins associate with LXXLL motifs on target cellular proteins to alter their function. Using a proteomic approach, we found the E6 oncoproteins of cutaneous papillomaviruses Bovine Papillomavirus Type 1 (BPV-1) E6 and human papillomavirus (HPV) types 1 and 8 (1E6 and 8E6) associated with the MAML1 transcriptional co-activator. All three E6 proteins bind to an acidic LXXLL motif at the carboxy-terminus of MAML1 and repress transactivation by MAML1. MAML1 is best known as the co-activator and effector of NOTCH-induced transcription, and BPV-1 E6 represses synthetic NOTCH-responsive promoters, endogenous NOTCH-responsive promoters, and is found in a complex with MAML1 in stably transformed cells. BPV-1-induced papillomas show characteristics of repressed NOTCH signal transduction, including suprabasal expression of integrins, talin and basal type keratins, and delayed expression of the NOTCH-dependent HES1 transcription factor. These observations give rise to a model whereby papillomavirus oncoproteins, including BPV-1 E6, and the cancer-associated HPV-8 E6 repress NOTCH-induced transcription, thereby delaying keratinocyte differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


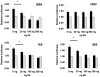

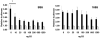



References
-
- zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in the causation of human cancers - a brief historical account. Virology. 2009 Feb 20;384(2):260–5. - PubMed
-
- Orth G. Genetics of epidermodysplasia verruciformis: Insights into host defense against papillomaviruses. Semin Immunol. 2006 Dec;18(6):362–74. - PubMed
-
- Green H. Terminal differentiation of cultured human epidermal cells. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):405–16. - PubMed
-
- Adams JC, Watt FM. Fibronectin inhibits the terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):307–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

