Inhibition of Gsk3β activity improves β-cell function in c-KitWv/+ male mice
- PMID: 22249311
- PMCID: PMC3940483
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.200
Inhibition of Gsk3β activity improves β-cell function in c-KitWv/+ male mice
Abstract
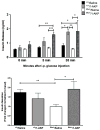
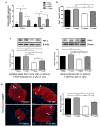
Previous studies have shown that the stem cell marker, c-Kit, is involved in glucose homeostasis. We recently reported that c-Kit(Wv/+) male mice displayed the onset of diabetes at 8 weeks of age; however, the mechanisms by which c-Kit regulates β-cell proliferation and function are unknown. The purpose of this study is to examine if c-Kit(Wv/+) mutation-induced β-cell dysfunction is associated with downregulation of the phospho-Akt/Gsk3β pathway in c-Kit(Wv/+) male mice. Histology and cell signaling were examined in C57BL/6J/Kit(Wv/+) (c-Kit(Wv/+)) and wild-type (c-Kit(+/+)) mice using immunofluorescence and western blotting approaches. The Gsk3β inhibitor, 1-azakenpaullone (1-AKP), was administered to c-Kit(Wv/+) and c-Kit(+/+) mice for 2 weeks, whereby alterations in glucose metabolism were examined and morphometric analyses were performed. A significant reduction in phosphorylated Akt was observed in the islets of c-Kit(Wv/+) mice (P<0.05) along with a decrease in phosphorylated Gsk3β (P<0.05), and cyclin D1 protein level (P<0.01) when compared with c-Kit(+/+) mice. However, c-Kit(Wv/+) mice that received 1-AKP treatment demonstrated normal fasting blood glucose with significantly improved glucose tolerance. 1-AKP-treated c-Kit(Wv/+) mice also showed increased β-catenin, cyclin D1 and Pdx-1 levels in islets, demonstrating that inhibition of Gsk3β activity led to increased β-cell proliferation and insulin secretion. These data suggest that c-Kit(Wv/+) male mice had alterations in the Akt/Gsk3β signaling pathway, which lead to β-cell dysfunction by decreasing Pdx-1 and cyclin D1 levels. Inhibition of Gsk3β could prevent the onset of diabetes by improving glucose tolerance and β-cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family of tyrosine kinase receptors: a Kit to fix the beta cell?Diabetologia. 2012 Aug;55(8):2092-5. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2611-4. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22696036
-
Stromal cell derived factor-1α promotes C-Kit+ cardiac stem/progenitor cell quiescence through casein kinase 1α and GSK3β.Stem Cells. 2014 Feb;32(2):487-99. doi: 10.1002/stem.1534. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24038789 Free PMC article.
-
Per-Arnt-Sim kinase regulates pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 protein stability via phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β in pancreatic β-cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 23;288(34):24825-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.495945. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23853095 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) induces mouse precartilaginous stem cell proliferation through TGF-β receptor II (TGFRII)-Akt-β-catenin signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jul 17;15(7):12665-76. doi: 10.3390/ijms150712665. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25036031 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of c-Kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model.Diabetologia. 2012 Aug;55(8):2214-25. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2566-5. Epub 2012 May 14. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22581040
Cited by
-
Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress is involved in the neuroprotective effect of aFGF in neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 29;8(37):60941-60953. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17524. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28977836 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetyl-L-cysteine treatment reduces beta-cell oxidative stress and pancreatic stellate cell activity in a high fat diet-induced diabetic mouse model.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 25;13:938680. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.938680. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36093092 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of γ-aminobutyric acid against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in RIN-m5F pancreatic cells.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018 Sep 3;15:60. doi: 10.1186/s12986-018-0299-2. eCollection 2018. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30202421 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Supplementation with Curcumin Reduce Circulating Levels of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β and Islet Amyloid Polypeptide in Adults with High Risk of Type 2 Diabetes and Alzheimer's Disease.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 9;12(4):1032. doi: 10.3390/nu12041032. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32283762 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family of tyrosine kinase receptors: a Kit to fix the beta cell?Diabetologia. 2012 Aug;55(8):2092-5. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2611-4. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22696036
References
-
- Hao E, Tyrberg B, Itkin-Ansari P, et al. Beta-cell differentiation from nonendocrine epithelial cells of the adult human pancreas. Nat Med. 2006;12:310–316. - PubMed
-
- Meier JJ, Bhushan A, Butler PC. The potential for stem cell therapy in diabetes. Pediatr Res. 2006;59(Part 2):65R–73R. - PubMed
-
- Jiang J, Au M, Lu K, et al. Generation of insulin-producing islet-like clusters from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25:1940–1953. - PubMed
-
- Bonner-Weir S, Sharma A. Pancreatic stem cells. J Pathol. 2002;197:519–526. - PubMed
-
- Heit JJ, Kim SK. Embryonic stem cells and islet replacement in diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes. 2004;5 (Suppl 2):5–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

