Age, microbiota, and T cells shape diverse individual IgA repertoires in the intestine
- PMID: 22249449
- PMCID: PMC3280880
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20111980
Age, microbiota, and T cells shape diverse individual IgA repertoires in the intestine
Abstract
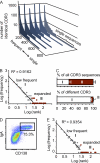
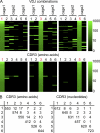
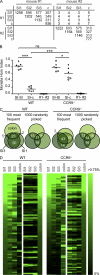
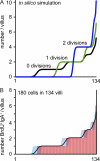
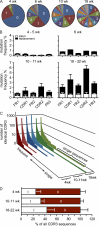
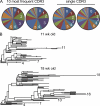
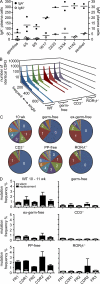
Intestinal immunoglobulin A (IgA) ensures host defense and symbiosis with our commensal microbiota. Yet previous studies hint at a surprisingly low diversity of intestinal IgA, and it is unknown to what extent the diverse Ig arsenal generated by somatic recombination and diversification is actually used. In this study, we analyze more than one million mouse IgA sequences to describe the shaping of the intestinal IgA repertoire, its determinants, and stability over time. We show that expanded and infrequent clones combine to form highly diverse polyclonal IgA repertoires with very little overlap between individual mice. Selective homing allows expanded clones to evenly seed the small but not large intestine. Repertoire diversity increases during aging in a dual process. On the one hand, microbiota-, T cell-, and transcription factor RORγt-dependent but Peyer's patch-independent somatic mutations drive the diversification of expanded clones, and on the other hand, new clones are introduced into the repertoire of aged mice. An individual's IgA repertoire is stable and recalled after plasma cell depletion, which is indicative of functional memory. These data provide a conceptual framework to understand the dynamic changes in the IgA repertoires to match environmental and intrinsic stimuli.
Figures


References
-
- Asahi Y., Yoshikawa T., Watanabe I., Iwasaki T., Hasegawa H., Sato Y., Shimada S., Nanno M., Matsuoka Y., Ohwaki M., et al. 2002. Protection against influenza virus infection in polymeric Ig receptor knockout mice immunized intranasally with adjuvant-combined vaccines. J. Immunol. 168:2930–2938 - PubMed
-
- Barone F., Vossenkamper A., Boursier L., Su W., Watson A., John S., Dunn-Walters D.K., Fields P., Wijetilleka S., Edgeworth J.D., Spencer J. 2011. IgA-producing plasma cells originate from germinal centers that are induced by B-cell receptor engagement in humans. Gastroenterology. 140:947–956 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.12.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

