Kuru: genes, cannibals and neuropathology
- PMID: 22249461
- PMCID: PMC5120877
- DOI: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182444efd
Kuru: genes, cannibals and neuropathology
Abstract
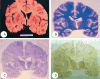
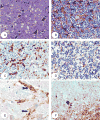
Kuru was the first human transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) or prion disease identified, occurring in the Fore linguistic group of Papua New Guinea. Kuru was a uniformly fatal cerebellar ataxic syndrome, usually followed by choreiform and athetoid movements. Kuru imposed a strong balancing selection on the Fore population, with individuals homozygous for the 129 Met allele of the gene (PRNP) encoding for prion protein (PrP) being the most susceptible. The decline in the incidence of kuru in the Fore has been attributed to the exhaustion of the susceptible genotype and ultimately by discontinuation of exposure via cannibalism. Neuropathologically, kuru-affected brains were characterized by widespread degeneration of neurons, astroglial and microglial proliferation, and the presence of amyloid plaques. These early findings have been confirmed and extended by recent immunohistochemical studies for the detection of the TSE-specific PrP (PrP). Confocal laser microscopy also showed the concentration of glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive astrocytic processes at the plaque periphery. The fine structure of plaques corresponds to that described earlier by light microscopy. The successful experimental transmission of kuru led to the awareness of its similarity to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease and formed a background against which the recent epidemics of iatrogenic and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease could be studied.
Figures


References
-
- Gajdusek DC, Gibbs CJ, Alpers MP. Experimental transmission of a kuru-like syndrome to chimpanzees. Nature. 1966;209:794–96. - PubMed
-
- Gibbs CJ, Jr, Gajdusek DC, Asher DM, et al. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (spongiform encephalopathy): Transmission to chimpanzee. Science. 1968;161:388–89. - PubMed
-
- Gajdusek DC. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science. 1977;197:943–60. - PubMed
-
- Prusiner SB. Prions. In: Jörnvall H, editor. Nobel Lectures, Physiology or Medicine 1996–2000. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co; 2003.
-
- Wüthrich K. NMR studies of structure and function of biological macromolecules. In: Frängsmyr T, editor. Les Prix Nobel The Nobel Prizes 2002. Stockholm, Sweden: Nobel Foundation; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

