Maternal zinc supplementation improves spatial memory in rat pups
- PMID: 22249889
- PMCID: PMC3362702
- DOI: 10.1007/s12011-012-9323-y
Maternal zinc supplementation improves spatial memory in rat pups
Abstract
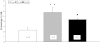
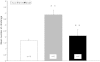
A large body of evidence supports an opinion that adequate dietary zinc is essential for prenatal and postnatal brain development. Behavioural effects of maternal supplementation with ZnSO(4) were analysed in rat pups with the Morris water task performance, a hole board and a T-maze. Wistar females during pregnancy and lactation received a drinking water solution of ZnSO(4) at doses of 16 mg/kg (group Zn16) or 32 mg/kg (group Zn32). Behavioural tests were conducted on the 4-week-old male rat pups. Zinc concentration in the serum, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of offsprings was determined by means of atomic absorption techniques. The Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test revealed an increase of climbing in the Zn16 group in comparison to the control group (Con) and the Zn32 group during the hole board test. ANOVA for repeated measures showed a significant memory improvement in both supplemented groups compared to the control in the probe trial on day 5 of the water maze test. ZnSO(4) treatment significantly elevated zinc levels in the rat serum. Follow-up data on brain content of zinc in the hippocampus revealed significant differences between the groups and in supplemented groups correlated with crossings above the original platform position. These findings suggest that pre- and postnatal zinc supplementation may improve cognitive development in rats.
Figures



References
-
- Halas ES, Wallwork JC, Sandstead HH. Mild zinc deficiency and undernutrition during the prenatal and postnatal periods in rats: effects on weight, food consumption, and brain catecholamine concentrations. J Nutr. 1982;112:542–551. - PubMed
-
- Tomat A, Elesgaray R, Zago V, Fasoli H, Fellet A, Balaszczuk AM, Schreier L, Costa MA, Arranz C. Exposure to zinc deficiency in fetal and postnatal life determines nitric oxide system activity and arterial blood pressure levels in adult rats. Br J Nutr. 2010;104:382–389. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510000759. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

