The use of 2,2'-dithiobis(5-nitropyridine) (DTNP) for deprotection and diselenide formation in protected selenocysteine-containing peptides
- PMID: 22249911
- PMCID: PMC3437994
- DOI: 10.1002/psc.1430
The use of 2,2'-dithiobis(5-nitropyridine) (DTNP) for deprotection and diselenide formation in protected selenocysteine-containing peptides
Abstract
In contrast to the large number of sidechain protecting groups available for cysteine derivatives in solid phase peptide synthesis, there is a striking paucity of analogous selenocysteine Se-protecting groups in the literature. However, the growing interest in selenocysteine-containing peptides and proteins requires a corresponding increase in availability of synthetic routes into these target molecules. It therefore becomes important to design new sidechain protection strategies for selenocysteine as well as multiple and novel deprotection chemistry for their removal. In this paper, we outline the synthesis of two new Fmoc selenocysteine derivatives [Fmoc-Sec(Meb) and Fmoc-Sec(Bzl)] to accompany the commercially available Fmoc-Sec(Mob) derivative and incorporate them into two model peptides. Sec-deprotection assays were carried out on these peptides using 2,2'-dithiobis(5-nitropyridine) (DTNP) conditions previously described by our group. The deprotective methodology was further evaluated as to its suitability towards mediating concurrent diselenide formation in oxytocin-templated target peptides. Sec(Mob) and Sec(Meb) were found to be extremely labile to the DTNP conditions whether in the presence or absence of thioanisole, whereas Sec(Bzl) was robust to DTNP in the absence of thioanisole but quite labile in its presence. In multiple Sec-containing model peptides, it was shown that bis-Sec(Mob)-containing systems spontaneously cyclize to the diselenide using 1 eq DTNP, whereas bis-Sec(Meb) and Sec(Bzl) models required additional manipulation to induce cyclization.
Copyright © 2012 European Peptide Society and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
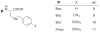
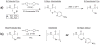

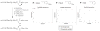

Similar articles
-
Facile removal of 4-methoxybenzyl protecting group from selenocysteine.J Pept Sci. 2019 Oct;25(10):e3209. doi: 10.1002/psc.3209. Epub 2019 Aug 13. J Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 31410953 Free PMC article.
-
Fmoc-Sec(Xan)-OH: synthesis and utility of Fmoc selenocysteine SPPS derivatives with acid-labile sidechain protection.J Pept Sci. 2015 Jan;21(1):53-9. doi: 10.1002/psc.2723. Epub 2014 Dec 11. J Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25504629 Free PMC article.
-
2,2'-Dithiobis(5-nitropyridine) (DTNP) as an effective and gentle deprotectant for common cysteine protecting groups.J Pept Sci. 2012 Jan;18(1):1-9. doi: 10.1002/psc.1403. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22083608 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and semisynthesis of selenopeptides and selenoproteins.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Oct;46:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.04.008. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29723718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenol protecting groups in organic chemistry: special emphasis on selenocysteine Se-protection in solid phase peptide synthesis.Molecules. 2011 Apr 18;16(4):3232-51. doi: 10.3390/molecules16043232. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 21512438 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
One-Pot Chemical Protein Synthesis Utilizing Fmoc-Masked Selenazolidine to Address the Redox Functionality of Human Selenoprotein F.Chemistry. 2022 Mar 16;28(16):e202200279. doi: 10.1002/chem.202200279. Epub 2022 Feb 19. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 35112407 Free PMC article.
-
Probing pattern and dynamics of disulfide bridges using synthesis and NMR of an ion channel blocker peptide toxin with multiple diselenide bonds.Chem Sci. 2016 Apr 21;7(4):2666-2673. doi: 10.1039/c5sc03995a. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 28660039 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Incorporation of Selenocysteine Using an Expanded Genetic Code and Palladium-Mediated Chemical Deprotection.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Jul 18;140(28):8807-8816. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b04603. Epub 2018 Jul 9. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29984990 Free PMC article.
-
2,2'-Dipyridyl diselenide: A chemoselective tool for cysteine deprotection and disulfide bond formation.J Pept Sci. 2020 Mar;26(3):e3236. doi: 10.1002/psc.3236. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 31856422 Free PMC article.
-
Can Selenoenzymes Resist Electrophilic Modification? Evidence from Thioredoxin Reductase and a Mutant Containing α-Methylselenocysteine.Biochemistry. 2020 Sep 15;59(36):3300-3315. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00608. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32845139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnér ES, Holmgren A. Physiological functions of thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:6102–6109. - PubMed
-
- Köhrle J. Local activation and inactivation of thyroid hormones: the deidodinase family. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 1999;151:103–119. - PubMed
-
- Burk RF, Hill KE. Selenoprotein P - A selenium-rich extracellular glycoprotein. J Nutr. 1994;124:1891–1897. - PubMed
-
- Isidro-Llobet A, Alvarez M, Albericio F. Amino acid protecting groups. Chem Rev. 2009;109:2455–2504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
