Absorption and metabolism of cis-9,trans-11-CLA and of its oxidation product 9,11-furan fatty acid by Caco-2 cells
- PMID: 22249938
- PMCID: PMC3311842
- DOI: 10.1007/s11745-012-3653-6
Absorption and metabolism of cis-9,trans-11-CLA and of its oxidation product 9,11-furan fatty acid by Caco-2 cells
Abstract
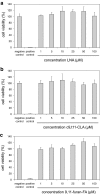
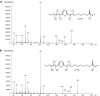
Furan fatty acids (furan-FA) can be formed by auto-oxidation of conjugated linoleic acids (CLA) and may therefore be ingested when CLA-containing foodstuff is consumed. Due to the presence of a furan ring structure, furan-FA may have toxic properties, however, these substances are toxicologically not well characterized so far. Here we show that 9,11-furan-FA, the oxidation product of the major CLA isomer cis-9,trans-11-CLA (c9,t11-CLA), is not toxic to human intestinal Caco-2 cells up to a level of 100 μM. Oil-Red-O staining indicated that 9,11-furan-FA as well as c9,t11-CLA and linoleic acid are taken up by the cells and stored in the form of triglycerides in lipid droplets. Chemical analysis of total cellular lipids revealed that 9,11-furan-FA is partially elongated probably by the enzymatic activity of cellular fatty acid elongases whereas c9,t11-CLA is partially converted to other isomers such as c9,c11-CLA or t9,t11-CLA. In the case of 9,11-furan-FA, there is no indication for any modification or activation of the furan ring system. From these results, we conclude that 9,11-furan-FA has no properties of toxicological relevance at least for Caco-2 cells which serve as a model for enterocytes of the human small intestine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In-vitro toxicological and proteomic analysis of furan fatty acids which are oxidative metabolites of conjugated linoleic acids.Lipids. 2012 Nov;47(11):1085-97. doi: 10.1007/s11745-012-3713-y. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Lipids. 2012. PMID: 22949068
-
Metabolic and growth inhibitory effects of conjugated fatty acids in the cell line HT-29 with special regard to the conversion of t11,t13-CLA.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Dec;1811(12):1070-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21889998
-
Potent inhibitory effect of trans9, trans11 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid on the growth of human colon cancer cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2006 Dec;17(12):830-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.01.007. Epub 2006 Mar 24. J Nutr Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16563722
-
Conjugated linoleic acids (CLA) as precursors of a distinct family of PUFA.Lipids. 2004 Nov;39(11):1143-6. doi: 10.1007/s11745-004-1341-0. Lipids. 2004. PMID: 15726830 Review.
-
Conjugated linoleic acid isomers: differences in metabolism and biological effects.Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):105-11. doi: 10.1002/biof.13. Biofactors. 2009. PMID: 19319853 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro digestion and culture in Caco-2 cells to assess the bioavailability of fatty acids: A case study in meat matrix enriched with ω-3 microcapsules.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Jun 17;12(9):6338-6352. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4241. eCollection 2024 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39554339 Free PMC article.
-
In-vitro toxicological and proteomic analysis of furan fatty acids which are oxidative metabolites of conjugated linoleic acids.Lipids. 2012 Nov;47(11):1085-97. doi: 10.1007/s11745-012-3713-y. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Lipids. 2012. PMID: 22949068
References
-
- Kepler CR, Hirons KP, McNeill JJ, Tove SB. Intermediates and products of the biohydrogenation of linoleic acid by Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. J Biol Chem. 1966;241:1350–1354. - PubMed
-
- Lampen A, Leifheit M, Voss J, Nau H. Molecular and cellular effects of cis-9,trans-11-conjugated linoleic acid in enterocytes: effects on proliferation, differentiation, and gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1735:30–40. - PubMed
-
- Kelley NS, Hubbard NE, Erickson KL. Conjugated linoleic acid isomers and cancer. J Nutr. 2007;137:2599–2607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

