The impact of stress on the life history strategies of African American adolescents: cognitions, genetic moderation, and the role of discrimination
- PMID: 22251000
- PMCID: PMC4324554
- DOI: 10.1037/a0026599
The impact of stress on the life history strategies of African American adolescents: cognitions, genetic moderation, and the role of discrimination
Abstract
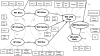
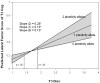
The impact of 3 different sources of stress--environmental, familial (e.g., low parental investment), and interpersonal (i.e., racial discrimination)--on the life history strategies (LHS) and associated cognitions of African American adolescents were examined over an 11-year period (5 waves, from age 10.5 to 21.5). Analyses indicated that each one of the sources of stress was associated with faster LHS cognitions (e.g., tolerance of deviance, willingness to engage in risky sex), which, in turn, predicted faster LHS behaviors (e.g., frequent sexual behavior). LHS, then, negatively predicted outcome (resilience) at age 21.5 (i.e., faster LHS → less resilience). In addition, presence of the risk ("sensitivity") alleles of 2 monoamine-regulating genes, the serotonin transporter gene (5HTTLPR) and the dopamine D4 receptor gene (DRD4), moderated the impact of perceived racial discrimination on LHS cognitions: Participants with more risk alleles (higher "sensitivity") reported faster LHS cognitions at age 18 and less resilience at age 21 if they had experienced higher amounts of discrimination and slower LHS and more resilience if they had experienced smaller amounts of discrimination. Implications for LHS theories are discussed.
Figures
Comment in
-
Differential susceptibility experiments: going beyond correlational evidence: comment on beyond mental health, differential susceptibility articles.Dev Psychol. 2012 May;48(3):769-74. doi: 10.1037/a0027536. Dev Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22545852
Similar articles
-
The effects of racial discrimination on the HIV-risk cognitions and behaviors of Black adolescents and young adults.Health Psychol. 2013 May;32(5):543-50. doi: 10.1037/a0028815. Health Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23646837 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in mothers' arginine vasopressin receptor 1a and dopamine receptor D4 genes predicts maternal sensitivity via social cognition.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Feb;16(2):233-240. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12326. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27581946 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine receptor gene d4 polymorphisms and early sexual onset: gender and environmental moderation in a sample of african-american youth.J Adolesc Health. 2014 Aug;55(2):235-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Adolesc Health. 2014. PMID: 24742759 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Genetic Influence on Psychological Resilience.Biol Res Nurs. 2019 Jan;21(1):61-71. doi: 10.1177/1099800418800396. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Biol Res Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30223673
-
[Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a consequence of the interaction between an individual genetic susceptibility, a traumatogenic event and a social context].Encephale. 2012 Oct;38(5):373-80. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Encephale. 2012. PMID: 23062450 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Association between resilience and a functional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter (SLC6A4) gene: A meta-analysis.EXCLI J. 2020 Aug 19;19:1174-1183. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-2660. eCollection 2020. EXCLI J. 2020. PMID: 33088257 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Moderation of the Impact of Parenting on Hostility toward Romantic Partners.J Marriage Fam. 2013 Apr;75(2):325-341. doi: 10.1111/jomf.12010. J Marriage Fam. 2013. PMID: 24379481 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate and non-candidate genes in behavior genetics.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013 Feb;23(1):57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 22878161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Environmental Risk and Externalizing Comorbidity on Internalizing Problems Among Economically Disadvantaged African American Youth.J Res Adolesc. 2016 Sep;26(3):552-566. doi: 10.1111/jora.12213. Epub 2015 Jul 8. J Res Adolesc. 2016. PMID: 27594775 Free PMC article.
-
Racial/ethnic discrimination and well-being during adolescence: A meta-analytic review.Am Psychol. 2018 Oct;73(7):855-883. doi: 10.1037/amp0000204. Epub 2018 Jul 19. Am Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30024216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Heart Association. Heart disease and stroke statistics. 2010 Retrieved from http://www.americanheart.org/downloadable/heart.
-
- Anderson E. Violence and the inner city street code. In: McCord J, editor. Violence and Childhood in the Inner City. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press; 1997. pp. 1–30.
-
- Belsky J, Pleuss Beyond diathesis-stress: Differential susceptibility to environmental influences. Psychological Bulletin. 2009;135(6):885–908. - PubMed

