Glial cells in (patho)physiology
- PMID: 22251135
- PMCID: PMC3304021
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07664.x
Glial cells in (patho)physiology
Abstract
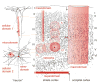
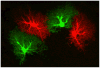
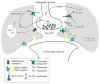
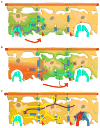
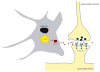
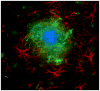
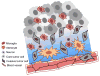
Neuroglial cells define brain homeostasis and mount defense against pathological insults. Astroglia regulate neurogenesis and development of brain circuits. In the adult brain, astrocytes enter into intimate dynamic relationship with neurons, especially at synaptic sites where they functionally form the tripartite synapse. At these sites, astrocytes regulate ion and neurotransmitter homeostasis, metabolically support neurons and monitor synaptic activity; one of the readouts of the latter manifests in astrocytic intracellular Ca(2+) signals. This form of astrocytic excitability can lead to release of chemical transmitters via Ca(2+) -dependent exocytosis. Once in the extracellular space, gliotransmitters can modulate synaptic plasticity and cause changes in behavior. Besides these physiological tasks, astrocytes are fundamental for progression and outcome of neurological diseases. In Alzheimer's disease, for example, astrocytes may contribute to the etiology of this disorder. Highly lethal glial-derived tumors use signaling trickery to coerce normal brain cells to assist tumor invasiveness. This review not only sheds new light on the brain operation in health and disease, but also points to many unknowns.
© 2012 The Authors. Journal of Neurochemistry © 2012 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures
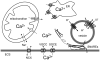
References
-
- Agulhon C, Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD. Hippocampal short- and long-term plasticity are not modulated by astrocyte Ca2+ signaling. Science. 2010;327:1250–1254. - PubMed
-
- Anlauf E, Derouiche A. Astrocytic exocytosis vesicles and glutamate: a high-resolution immunofluorescence study. Glia. 2005;49:96–106. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG. Glutamate-dependent astrocyte modulation of synaptic transmission between cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:2129–2142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

