Effects of hallucinogenic agents mescaline and phencyclidine on zebrafish behavior and physiology
- PMID: 22251567
- PMCID: PMC3294104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2012.01.003
Effects of hallucinogenic agents mescaline and phencyclidine on zebrafish behavior and physiology
Abstract
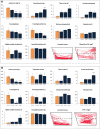
Mescaline and phencyclidine (PCP) are potent hallucinogenic agents affecting human and animal behavior. As their psychotropic effects remain poorly understood, further research is necessary to characterize phenotypes they evoke in various animal models. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) are rapidly emerging as a new model organism for neuroscience research. Here, we examine the effects of mescaline (5-20mg/l) and PCP (0.5-3mg/l) in several zebrafish paradigms, including the novel tank, open field and shoaling tests. Mescaline and PCP dose-dependently increased top activity in the novel tank test, also reducing immobility and disrupting the patterning of zebrafish swimming, as assessed by ethograms. PCP, but not mescaline, evoked circling behavior in the open field test. At the highest doses tested, mescaline markedly increased, while PCP did not affect, zebrafish shoaling behavior. Finally, 20mg/l mescaline did not alter, and 3mg/l PCP elevated, whole-body cortisol levels. Overall, our studies indicate high sensitivity of zebrafish models to hallucinogenic compounds with complex behavioral and physiological effects.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Aanonsen LM, Wilcox GL. Nociceptive action of excitatory amino acids in the mouse: effects of spinally administered opioids, phencyclidine and sigma agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;243:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Abramson HA, Gettner HH, Carone PA, Rolo A, Krinsky L. The intracranial injection of drug in goldfish. I: Hallucinogens and their antagonism to smooth muscle activity. J Asthma Res. 1979;16:55–61. - PubMed
-
- Airhart MJ, Lee DH, Wilson TD, Miller BE, Miller MN, Skalko RG. Movement disorders and neurochemical changes in zebrafish larvae after bath exposure to fluoxetine (PROZAC) Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2007;29:652–64. - PubMed
-
- Ali SF, Newport GD, Bracha HS. Phencyclidine and (+)-MK-801-induced circling preference: correlation with monoamine levels in striatum of the rat brain. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1994;16:335–42. - PubMed
-
- Ali SF, Kordsmeier KJ, Gough B. Drug-induced circling preference in rats. Correlation with monoamine levels. Mol Neurobiol. 1995;11:145–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

