Plasma membrane calcium pump (PMCA) isoform 4 is targeted to the apical membrane by the w-splice insert from PMCA2
- PMID: 22252018
- PMCID: PMC3279596
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.12.010
Plasma membrane calcium pump (PMCA) isoform 4 is targeted to the apical membrane by the w-splice insert from PMCA2
Abstract
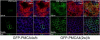
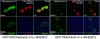
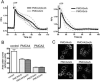
Local Ca(2+) signaling requires proper targeting of the Ca(2+) signaling toolkit to specific cellular locales. Different isoforms of the plasma membrane Ca(2+) pump (PMCA) are responsible for Ca(2+) extrusion at the apical and basolateral membrane of polarized epithelial cells, but the mechanisms and signals for differential targeting of the PMCAs are not well understood. Recent work demonstrated that the alternatively spliced w-insert in PMCA2 directs this pump to the apical membrane. We now show that inserting the w-insert into the corresponding location of the PMCA4 isoform confers apical targeting to this normally basolateral pump. Mutation of a di-leucine motif in the C-tail thought to be important for basolateral targeting did not enhance apical localization of the chimeric PMCA4(2w)/b. In contrast, replacing the C-terminal Val residue by Leu to optimize the PDZ ligand site for interaction with the scaffolding protein NHERF2 enhanced the apical localization of PMCA4(2w)/b, but not of PMCA4x/b. Functional studies showed that both apical PMCA4(2w)/b and basolateral PMCA4x/b handled ATP-induced Ca(2+) signals with similar kinetics, suggesting that isoform-specific functional characteristics are retained irrespective of membrane targeting. Our results demonstrate that the alternatively spliced w-insert provides autonomous apical targeting information in the PMCA without altering its functional characteristics.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Alternative splicing of the first intracellular loop of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase isoform 2 alters its membrane targeting.J Biol Chem. 2003 May 16;278(20):18464-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301482200. Epub 2003 Mar 6. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12624087
-
Apical scaffolding protein NHERF2 modulates the localization of alternatively spliced plasma membrane Ca2+ pump 2B variants in polarized epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31704-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164137. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663896 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of apical membrane enrichment and retention of plasma membrane Ca ATPase splice variants by the PDZ-domain protein NHERF2.Commun Integr Biol. 2011 May;4(3):340-3. doi: 10.4161/cib.4.3.15040. Epub 2011 May 1. Commun Integr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21980575 Free PMC article.
-
The plasma membrane calcium pump in the hearing process: physiology and pathology.Sci China Life Sci. 2011 Aug;54(8):686-90. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4200-z. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Sci China Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21786191 Review.
-
The plethora of PMCA isoforms: Alternative splicing and differential expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1853(9):2018-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.12.020. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25535949 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for a role of plasma membrane calcium pumps in neurodegenerative disease: Recent developments.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Jan 10;663:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.035. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 28827127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Whitish Inner Mantle of the Giant Clam, Tridacna squamosa, Expresses an Apical Plasma Membrane Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA) Which Displays Light-Dependent Gene and Protein Expressions.Front Physiol. 2017 Oct 10;8:781. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00781. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29066980 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma Membrane Ca2+ Pump PMCA4z Is More Active Than Splicing Variant PMCA4x.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Aug 26;15:668371. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.668371. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34512262 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma membrane calcium ATPases as novel candidates for therapeutic agent development.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2013;16(2):190-206. doi: 10.18433/j3z011. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2013. PMID: 23958189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bootman MD, Lipp P, Berridge MJ. The organisation and functions of local Ca2+ signals. J. Cell Sci. 2001;114:2213–2222. - PubMed
-
- Kiselyov K, Wang X, Shin DM, Zang W, Muallem S. Calcium signaling complexes in microdomains of polarized secretory cells. Cell Calcium. 2006;40:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Brini M, Carafoli E. Calcium pumps in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009;89:1341–1378. - PubMed
-
- Strehler EE, Zacharias DA. Role of alternative splicing in generating isoform diversity among plasma membrane calcium pumps. Physiol. Rev. 2001;81:21–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

