Frontiers in optical imaging of cerebral blood flow and metabolism
- PMID: 22252238
- PMCID: PMC3390808
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.195
Frontiers in optical imaging of cerebral blood flow and metabolism
Abstract
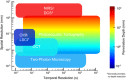
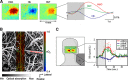
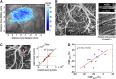
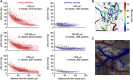
In vivo optical imaging of cerebral blood flow (CBF) and metabolism did not exist 50 years ago. While point optical fluorescence and absorption measurements of cellular metabolism and hemoglobin concentrations had already been introduced by then, point blood flow measurements appeared only 40 years ago. The advent of digital cameras has significantly advanced two-dimensional optical imaging of neuronal, metabolic, vascular, and hemodynamic signals. More recently, advanced laser sources have enabled a variety of novel three-dimensional high-spatial-resolution imaging approaches. Combined, as we discuss here, these methods are permitting a multifaceted investigation of the local regulation of CBF and metabolism with unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution. Through multimodal combination of these optical techniques with genetic methods of encoding optical reporter and actuator proteins, the future is bright for solving the mysteries of neurometabolic and neurovascular coupling and translating them to clinical utility.
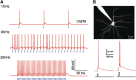
Figures
References
-
- Adams SR, Tsien RY. Controlling cell chemistry with caged compounds. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:755–784. - PubMed
-
- Akemann W, Mutoh H, Perron A, Rossier J, Knopfel T. Imaging brain electric signals with genetically targeted voltage-sensitive fluorescent proteins. Nat Methods. 2010;7:643–649. - PubMed
-
- Allaman I, Belanger M, Magistretti PJ. Astrocyte-neuron metabolic relationships: for better and for worse. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34:76–87. - PubMed
-
- Ayata C, Dunn AK, Gursoy OY, Huang Z, Boas DA, Moskowitz MA. Laser speckle flowmetry for the study of cerebrovascular physiology in normal and ischemic mouse cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24:744–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- EB007279/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB00790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB007279/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 NS067050/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB001954/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99NS067050/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 NS067050/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

