Computer-assisted surgery as indication of choice: total knee arthroplasty in case of retained hardware or extra-articular deformity
- PMID: 22252414
- PMCID: PMC3385888
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1476-3
Computer-assisted surgery as indication of choice: total knee arthroplasty in case of retained hardware or extra-articular deformity
Abstract
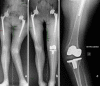
Purpose: The use of traditional cutting guides during knee arthroplasty in some cases could be extremely difficult, if not impossible, because of angular deformities, IM sclerosis, long-stemmed hip implants, or hardware within the femoral canal that cannot be removed. In these difficult cases navigation-assisted knee arthroplasty should be considered as an effective and appealing option.
Methods: We present 14 cases in which ideal mechanical and prosthetic alignment was achieved with different image-free, computer-assisted navigation systems, because of an extra-articular deformity (group A, nine patients) or because of a retained implant or hardware (group B, five patients).
Results: After a mean follow-up of 28 months (range 12-53 months), the average knee score increased overall from a mean of 33 points (range 12-63) to 78 points (range 63-90). The average functional score improved from a mean of 32 points (range 10-65) to 72 points (range 40-90). The postoperative mechanical axis ranged between 3° of varus and 3° of valgus. There was an implant revision in one patient who had a traumatic rupture of medial collateral ligament, which occurred 27 months after the index procedure.
Conclusions: Based on our results we think that the navigation-assisted technique provides an alternative approach to the traditional instrumentation for treating these difficult patients in an effective and less invasive manner.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Total knee arthroplasty with patient-specific instruments improves function and restores limb alignment in patients with extra-articular deformity.Knee. 2013 Dec;20(6):407-11. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Knee. 2013. PMID: 23899651
-
Simultaneous femoral osteotomy and total knee arthroplasty for treatment of osteoarthritis associated with severe extra-articular deformity.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000 Mar;82(3):342-8. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200003000-00005. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. PMID: 10724226
-
Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty in knees with osteoarthritis due to extra-articular deformity.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012 Mar;20(3):546-51. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1602-1. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012. PMID: 21800169
-
["Ligament balancing" and varus deformity in total knee arthroplasty].Orthopade. 2007 Jul;36(7):643-4, 646-9. doi: 10.1007/s00132-007-1111-6. Orthopade. 2007. PMID: 17593349 Review. German.
-
Progress in Computer-Assisted Navigation for Total Knee Arthroplasty in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular Deformity.Orthop Surg. 2024 Nov;16(11):2608-2619. doi: 10.1111/os.14216. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 39223445 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complex Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with Achondroplasia, Osteoarthritis, and Severe Coronal Instability.Arthroplast Today. 2021 Feb 24;8:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2020.12.023. eCollection 2021 Apr. Arthroplast Today. 2021. PMID: 33681436 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Radiological Outcomes of Computer-Assisted Navigation in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Extra-articular Deformity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Orthop Surg. 2024 Jun;16(3):430-440. doi: 10.4055/cios23261. Epub 2024 May 2. Clin Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38827763 Free PMC article.
-
Does computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty improve the overall component position and patient function?Int Orthop. 2014 Feb;38(2):251-7. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-1996-0. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 23842630 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Accuracy of CT-based patient-specific guides for total knee arthroplasty in patients with post-traumatic osteoarthritis.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015 Dec;25(8):1313-20. doi: 10.1007/s00590-015-1677-3. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015. PMID: 26265403
-
Complex primary total knee arthroplasty with constrained condylar knee in post-traumatic arthritis: a retrospective comparison between 3D-printed patient-specific instrumentation and conventional instrumentation.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 May 27;20(1):524. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05909-7. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40420245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(5):709–714. - PubMed
-
- Insall JN, Easley ME (2001) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty In: Insall JN, Scott WN (eds). Surgery of the knee, 3rd edn. Churchill Livingston, Philadelphia, p 1578
-
- Stulberg SD, Loan P, Sarin V. Computer-assisted navigation in total knee replacement: results of an initial experience in thirty-five patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(Suppl 2):90–98. - PubMed
-
- Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW. The efficacy of intramedullary femoral alignment in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop. 1995;321:117–121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

