Pharmacokinetics of and short-term virologic response to low-dose 400-milligram once-daily raltegravir maintenance therapy
- PMID: 22252825
- PMCID: PMC3318383
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05694-11
Pharmacokinetics of and short-term virologic response to low-dose 400-milligram once-daily raltegravir maintenance therapy
Abstract
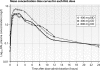
Because studies showed similar viral suppression with lower raltegravir doses and because Asians usually have high antiretroviral concentrations, we explored low-dose raltegravir therapy in Thais. Nineteen adults on raltegravir at 400 mg twice daily (BID) with HIV RNA loads of <50 copies/ml were randomized to receive 400 mg once daily (QD) or 800 mg QD for 2 weeks, followed by the other dosing for 2 weeks. Intensive pharmacokinetic analyses were performed, and HIV RNA was monitored. Two patients were excluded from the 400-mg QD analysis due to inevaluable pharmacokinetic data. The mean patient weight was 58 kg. Mean pharmacokinetic values were as follows: for raltegravir given at 400 mg BID, the area under the concentration-time curve from 0 to 12 h (AUC₀₋₁₂) was 15.6 mg/liter-h and the minimum plasma drug concentration (C(trough)) was 0.22 mg/liter; for raltegravir given at 800 mg QD, the AUC₀₋₂₄ was 33.6 mg/liter-h and the C(trough) was 0.06 mg/liter; and for raltegravir given at 400 mg QD, the AUC₀₋₂₄ was 18.6 mg/liter-h and the C(trough) was 0.08 mg/liter. The HIV RNA load was <50 copies/ml at each dose level. Compared to the adjusted AUC₀₋₂₄ for Westerners on raltegravir at 400 mg BID, Thais on the same dose had double the AUC₀₋₂₄ and those on raltegravir at 400 mg QD had a similar AUC₀₋₂₄. More patients had a C(trough) of <0.021 mg/liter on raltegravir at 400 mg QD (9/17 patients) than on raltegravir at 800 mg QD (1/19 patients) or 400 mg BID (0/19 patients). Seventeen patients used raltegravir at 400 mg QD for a median of 35 weeks; two had confirmed HIV RNA loads between 50 and 200 copies/ml, and both had low C(trough) values. Low-dose raltegravir could be a cost-saving option for maintenance therapy in Asians or persons with low body weight. However, raltegravir at 400 mg QD was associated with a low C(trough) and with a risk for HIV viremia. Raltegravir at 200 or 300 mg BID should be studied, but new raltegravir formulations will be needed.
Figures
References
-
- Ananworanich J, et al. 2004. Creation of a drug fund for post-clinical trial access to antiretrovirals. Lancet 364:101–102 - PubMed
-
- Autar RS, et al. 2005. Interindividual variability of once-daily ritonavir boosted saquinavir pharmacokinetics in Thai and UK patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 56:908–913 - PubMed
-
- Avihingsanon A, et al. 2009. A low dose of ritonavir-boosted atazanavir provides adequate pharmacokinetic parameters in HIV-1-infected Thai adults. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 85:402–408 - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo D, et al. 2010. Exposure-related effects of atazanavir on the pharmacokinetics of raltegravir in HIV-1-infected patients. Ther. Drug Monit. 32:782–786 - PubMed
-
- Cooper DA, et al. 2008. Subgroup and resistance analyses of raltegravir for resistant HIV-1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 359:355–365 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

