Attenuation-based dual-fluorescent-protein reporter for screening translation inhibitors
- PMID: 22252829
- PMCID: PMC3318315
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05395-11
Attenuation-based dual-fluorescent-protein reporter for screening translation inhibitors
Abstract
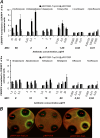
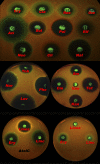
A reporter construct was created on the basis of the transcription attenuator region of the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. Dual-fluorescent-protein genes for red fluorescent protein and cerulean fluorescent protein were used as a sensor and internal control of gene expression. The sequence of the attenuator was modified to avoid tryptophan sensitivity while preserving sensitivity to ribosome stalling. Antimicrobial compounds which cause translation arrest at the stage of elongation induce the reporter both in liquid culture and on an agar plate. This reporter could be used for high-throughput screening of translation inhibitors.
Figures

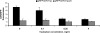


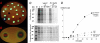
References
-
- Anko ML, Kurittu J, Karp M. 2002. An Escherichia coli biosensor strain for amplified and high throughput detection of antimicrobial agents. J. Biomol. Screen. 7:119–125 - PubMed
-
- Beatty KE, Xie F, Wang Q, Tirrell DA. 2005. Selective dye-labeling of newly synthesized proteins in bacterial cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127:14150–14151 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

