SNP calling using genotype model selection on high-throughput sequencing data
- PMID: 22253293
- PMCID: PMC3338331
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts001
SNP calling using genotype model selection on high-throughput sequencing data
Abstract
Motivation: A review of the available single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) calling procedures for Illumina high-throughput sequencing (HTS) platform data reveals that most rely mainly on base-calling and mapping qualities as sources of error when calling SNPs. Thus, errors not involved in base-calling or alignment, such as those in genomic sample preparation, are not accounted for.
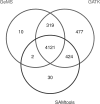
Results: A novel method of consensus and SNP calling, Genotype Model Selection (GeMS), is given which accounts for the errors that occur during the preparation of the genomic sample. Simulations and real data analyses indicate that GeMS has the best performance balance of sensitivity and positive predictive value among the tested SNP callers.
Availability: The GeMS package can be downloaded from https://sites.google.com/a/bioinformatics.ucr.edu/xinping-cui/home/software or http://computationalbioenergy.org/software.html.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
References
-
- Chakravarti A. Single nucleotide polymorphisms:… to a future of genetic medicine. Nature. 2001;409:822–823. - PubMed
-
- Dixon W.J. Analysis of extreme values. Ann. Math. Stat. 1950;21:488–506.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources