Angiotensin II-dependent transcriptional activation of human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene by a 25-kDa cAMP-responsive element modulator protein isoform and Yin Yang 1
- PMID: 22253417
- PMCID: PMC3281547
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-1744
Angiotensin II-dependent transcriptional activation of human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene by a 25-kDa cAMP-responsive element modulator protein isoform and Yin Yang 1
Abstract
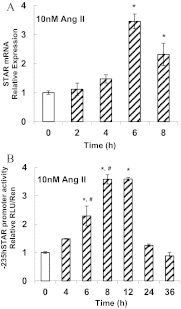
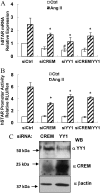
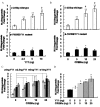
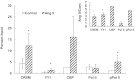
Transcriptional activation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR) gene is a critical component in the angiotensin II (Ang II)-dependent increase in aldosterone biosynthesis in the adrenal gland. The purpose of this study was to define the molecular mechanisms that mediate the Ang II-dependent increase in STARD1 gene (STAR) expression in H295R human adrenocortical cells. Mutational analysis of the STAR proximal promoter revealed that a nonconsensus cAMP-responsive element located at -78 bp relative to the transcription start site (-78CRE) is required for the Ang II-stimulated STAR reporter gene activity. DNA immunoaffinity chromatography identified a 25-kDa cAMP-responsive element modulator isoform and Yin Yang 1 (YY1) as -78CRE DNA-binding proteins, and Ang II treatment of H295R cells increased expression of that 25-kDa CREM isoform. Small interfering RNA silencing of CREM and YY1 attenuated the Ang II-dependent increases in STAR reporter gene activity and STAR mRNA levels. Conversely, overexpression of CREM and YY1 in COS-1 cells resulted in transactivation of STAR reporter gene activity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis demonstrated recruitment of CREM and YY1 to the STAR promoter along with increased association of the coactivator cAMP response element-binding protein-binding protein (CBP) and increased phosphorylated RNA polymerase II after Ang II treatment. Together our data reveal that the Ang II-stimulated increase in STAR expression in H295R cells requires 25 kDa CREM and YY1. The recruitment of these transcription factors to the STAR proximal promoter results in association of CBP and activation of RNA polymerase II leading to increased STAR transcription.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of steroidogenesis and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by a member of the cAMP response-element binding protein family.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Jan;16(1):184-99. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0759. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11773448
-
CREM confers cAMP responsiveness in human steroidogenic acute regulatory protein expression in NCI-H295R cells rather than SF-1/Ad4BP.J Endocrinol. 2006 Oct;191(1):327-37. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06601. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 17065415
-
Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) enhances cAMP-responsive element binding (CREB) protein phosphorylation and phospho-CREB interaction with the mouse steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene promoter.Endocrinology. 2005 Mar;146(3):1348-56. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0761. Epub 2004 Nov 18. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15550512
-
The expanding family of CREB/CREM transcription factors that are involved with spermatogenesis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002 Feb 22;187(1-2):115-24. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00696-7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11988318 Review.
-
Role of basic leucine zipper proteins in transcriptional regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009 Apr 10;302(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2008.12.009. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19150388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nicotine Suppressed Fetal Adrenal StAR Expression via YY1 Mediated-Histone Deacetylation Modification Mechanism.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 3;17(9):1477. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091477. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27598153 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-DNA Interactions at the Opossum Npt2a Promoter are Dependent upon NHERF-1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):1-12. doi: 10.1159/000445601. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27322746 Free PMC article.
-
SFMBT2 (Scm-like with four mbt domains 2) negatively regulates cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48250-48264. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10198. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27340776 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of angiotensin II-responsive circadian clock gene expression in adrenal zona glomerulosa cells and human adrenocortical H295R cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 26;16:1525844. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1525844. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40206597 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of adrenocortical steroid hormone production by RhoA-diaphanous 1 signaling and the cytoskeleton.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 May 22;371(1-2):79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.11.014. Epub 2012 Nov 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23186810 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Parker KL, Schimmer BP. 1995. Transcriptional regulation of the genes encoding the cytochrome P-450 steroid hydroxylases. Vitam Horm 51:339–370 - PubMed
-
- Stocco DM, Clark BJ. 1996. Regulation of the acute production of steroids in steroidogenic cells. Endocr Rev 17:221–244 - PubMed
-
- Clark BJ, Wells J, King SR, Stocco DM. 1994. The purification, cloning, and expression of a novel luteinizing hormone-induced mitochondrial protein in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Characterization of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR). J Biol Chem 269:28314–28322 - PubMed
-
- Lin D, Sugawara T, Strauss JF, 3rd, Clark BJ, Stocco DM, Saenger P, Rogol A, Miller WL. 1995. Role of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein in adrenal and gonadal steroidogenesis. Science 267:1828–1831 - PubMed
-
- Epstein LF, Alberta JA, Pon LA, Orme-Johnson NR. 1989. Subcellular localization of a protein produced in adrenal cortex cells in response to ACTH. Endocr Res 15:117–127 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

