An siRNA screen in pancreatic beta cells reveals a role for Gpr27 in insulin production
- PMID: 22253604
- PMCID: PMC3257298
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002449
An siRNA screen in pancreatic beta cells reveals a role for Gpr27 in insulin production
Abstract
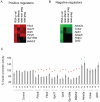
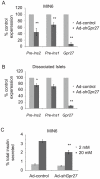
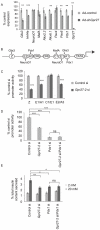
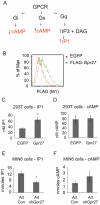
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes in the United States is projected to double or triple by 2050. We reasoned that the genes that modulate insulin production might be new targets for diabetes therapeutics. Therefore, we developed an siRNA screening system to identify genes important for the activity of the insulin promoter in beta cells. We created a subclone of the MIN6 mouse pancreatic beta cell line that expresses destabilized GFP under the control of a 362 base pair fragment of the human insulin promoter and the mCherry red fluorescent protein under the control of the constitutively active rous sarcoma virus promoter. The ratio of the GFP to mCherry fluorescence of a cell indicates its insulin promoter activity. As G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) have emerged as novel targets for diabetes therapies, we used this cell line to screen an siRNA library targeting all known mouse GPCRs. We identified several known GPCR regulators of insulin secretion as regulators of the insulin promoter. One of the top positive regulators was Gpr27, an orphan GPCR with no known role in beta cell function. We show that knockdown of Gpr27 reduces endogenous mouse insulin promoter activity and glucose stimulated insulin secretion. Furthermore, we show that Pdx1 is important for Gpr27's effect on the insulin promoter and insulin secretion. Finally, the over-expression of Gpr27 in 293T cells increases inositol phosphate levels, while knockdown of Gpr27 in MIN6 cells reduces inositol phosphate levels, suggesting this orphan GPCR might couple to Gq/11. In summary, we demonstrate a MIN6-based siRNA screening system that allows rapid identification of novel positive and negative regulators of the insulin promoter. Using this system, we identify Gpr27 as a positive regulator of insulin production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Narayan KM, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ, Sorensen SW, Williamson DF. Lifetime risk for diabetes mellitus in the United States. JAMA. 2003;290:1884–1890. - PubMed
-
- UKPDS. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki J, Araki K, Yamato E, Ikegami H, Asano T, et al. Establishment of a pancreatic beta cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion: special reference to expression of glucose transporter isoforms. Endocrinology. 1990;127:126–132. - PubMed
-
- Odagiri H, Wang J, German MS. Function of the human insulin promoter in primary cultured islet cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:1909–1915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

