Generation of long insert pairs using a Cre-LoxP Inverse PCR approach
- PMID: 22253722
- PMCID: PMC3253782
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029437
Generation of long insert pairs using a Cre-LoxP Inverse PCR approach
Abstract
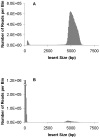
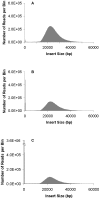
Large insert mate pair reads have a major impact on the overall success of de novo assembly and the discovery of inherited and acquired structural variants. The positional information of mate pair reads generally improves genome assembly by resolving repeat elements and/or ordering contigs. Currently available methods for building such libraries have one or more of limitations, such as relatively small insert size; unable to distinguish the junction of two ends; and/or low throughput. We developed a new approach, Cre-LoxP Inverse PCR Paired-End (CLIP-PE), which exploits the advantages of (1) Cre-LoxP recombination system to efficiently circularize large DNA fragments, (2) inverse PCR to enrich for the desired products that contain both ends of the large DNA fragments, and (3) the use of restriction enzymes to introduce a recognizable junction site between ligated fragment ends and to improve the self-ligation efficiency. We have successfully created CLIP-PE libraries up to 22 kb that are rich in informative read pairs and low in small fragment background. These libraries have demonstrated the ability to improve genome assemblies. The CLIP-PE methodology can be implemented with existing and future next-generation sequencing platforms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preparing Mate-Paired Illumina Libraries Using Cre Recombinase.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1642:247-261. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7169-5_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28815505
-
Preparing Fosmid Mate-Paired Libraries Using Cre-LoxP Recombination.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1642:263-284. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7169-5_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28815506
-
Illumina mate-paired DNA sequencing-library preparation using Cre-Lox recombination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(3):e24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1000. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22127871 Free PMC article.
-
Cre/loxP-mediated chromosome engineering of the mouse genome.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(178):29-48. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-35109-2_2. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17203650 Review.
-
Cre Recombinase.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Feb;3(1):MDNA3-0014-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MDNA3-0014-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104563 Review.
Cited by
-
A full-body transcriptome and proteome resource for the European common carp.BMC Genomics. 2016 Sep 2;17(1):701. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3038-y. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27590662 Free PMC article.
-
High-Quality Draft Genome Sequence of Fischerella thermalis JSC-11, a Siderophilic Cyanobacterium with Bioremediation Potential.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):e0076122. doi: 10.1128/mra.00761-22. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2022. PMID: 36301089 Free PMC article.
-
L_RNA_scaffolder: scaffolding genomes with transcripts.BMC Genomics. 2013 Sep 8;14:604. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-604. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24010822 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B X-interacting protein promotes the formation of the insulin gene-transcribing protein complex Pdx-1/Neurod1 in animal pancreatic β-cells.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):2053-2065. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.809582. Epub 2017 Dec 19. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29259128 Free PMC article.
-
Validation and genotyping of multiple human polymorphic inversions mediated by inverted repeats reveals a high degree of recurrence.PLoS Genet. 2014 Mar 20;10(3):e1004208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004208. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24651690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng P, Wei CL, Sung WK, Chiu KP, Lipovich L, et al. Gene identification signature (GIS) analysis for transcriptome characterization and genome annotation. Nature Methods. 2005;2:105–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

