SARS coronavirus 3b accessory protein modulates transcriptional activity of RUNX1b
- PMID: 22253733
- PMCID: PMC3257236
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029542
SARS coronavirus 3b accessory protein modulates transcriptional activity of RUNX1b
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(3). doi:10.1371/annotation/64ae6047-0f9b-4d17-a065-e08c153aa435. Agnihotram, Sudhakar [corrected to Agnihothram, Sudhakar]
Abstract
Background: The causative agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) genome encodes several unique group specific accessory proteins with unknown functions. Among them, accessory protein 3b (also known as ORF4) was lately identified as one of the viral interferon antagonist. Recently our lab uncovered a new role for 3b in upregulation of AP-1 transcriptional activity and its downstream genes. Thus, we believe that 3b might play an important role in SARS-CoV pathogenesis and therefore is of considerable interest. The current study aims at identifying novel host cellular interactors of the 3b protein.
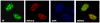
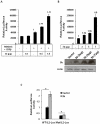
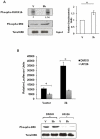
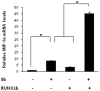
Methodology/principal findings: In this study, using yeast two-hybrid and co-immunoprecipitation techniques, we have identified a host transcription factor RUNX1b (Runt related transcription factor, isoform b) as a novel interacting partner for SARS-CoV 3b protein. Chromatin immunoprecipitaion (ChIP) and reporter gene assays in 3b expressing jurkat cells showed recruitment of 3b on the RUNX1 binding element that led to an increase in RUNX1b transactivation potential on the IL2 promoter. Kinase assay and pharmacological inhibitor treatment implied that 3b also affect RUNX1b transcriptional activity by regulating its ERK dependent phosphorylation levels. Additionally, mRNA levels of MIP-1α, a RUNX1b target gene upregulated in SARS-CoV infected monocyte-derived dendritic cells, were found to be elevated in 3b expressing U937 monocyte cells.
Conclusions/significance: These results unveil a novel interaction of SARS-CoV 3b with the host factor, RUNX1b, and speculate its physiological relevance in upregulating cytokines and chemokine levels in state of SARS virus infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Accessory proteins of SARS-CoV and other coronaviruses.Antiviral Res. 2014 Sep;109:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.06.013. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24995382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV accessory protein 3b induces AP-1 transcriptional activity through activation of JNK and ERK pathways.Biochemistry. 2011 Jun 21;50(24):5419-25. doi: 10.1021/bi200303r. Epub 2011 May 31. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21561061
-
The nonstructural protein 8 (nsp8) of the SARS coronavirus interacts with its ORF6 accessory protein.Virology. 2007 Sep 30;366(2):293-303. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2007.04.029. Epub 2007 May 25. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17532020 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial location of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 3b protein.Mol Cells. 2006 Apr 30;21(2):186-91. Mol Cells. 2006. PMID: 16682811
-
SARS coronavirus accessory proteins.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.10.009. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18045721 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An immune epigenetic insight to COVID-19 infection.Epigenomics. 2021 Mar;13(6):465-480. doi: 10.2217/epi-2020-0349. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Epigenomics. 2021. PMID: 33685230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accessory proteins of SARS-CoV and other coronaviruses.Antiviral Res. 2014 Sep;109:97-109. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.06.013. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Antiviral Res. 2014. PMID: 24995382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of Coronavirus Accessory Proteins: Overview of the State of the Art.Viruses. 2021 Jun 13;13(6):1139. doi: 10.3390/v13061139. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34199223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-Coronavirus Open Reading Frame-3a drives multimodal necrotic cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 5;9(9):904. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0917-y. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30185776 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecies Jumping of Bat Coronaviruses.Viruses. 2021 Oct 29;13(11):2188. doi: 10.3390/v13112188. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34834994 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drosten C, Gunther S, Preiser W, van der Werf S, Brodt HR, et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, Nix WA, Campagnoli R, et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
-
- Marra MA, Jones SJ, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks-Wilson A, et al. The Genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

