CD14 deficiency impacts glucose homeostasis in mice through altered adrenal tone
- PMID: 22253759
- PMCID: PMC3258240
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029688
CD14 deficiency impacts glucose homeostasis in mice through altered adrenal tone
Abstract
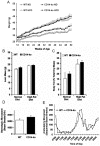
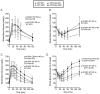
The toll-like receptors comprise one of the most conserved components of the innate immune system, signaling the presence of molecules of microbial origin. It has been proposed that signaling through TLR4, which requires CD14 to recognize bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), may generate low-grade inflammation and thereby affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. To examine the long-term influence of partial innate immune signaling disruption on glucose homeostasis, we analyzed knockout mice deficient in CD14 backcrossed into the diabetes-prone C57BL6 background at 6 or 12 months of age. CD14-ko mice, fed either normal or high-fat diets, displayed significant glucose intolerance compared to wild type controls. They also displayed elevated norepinephrine urinary excretion and increased adrenal medullary volume, as well as an enhanced norepinephrine secretory response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. These results point out a previously unappreciated crosstalk between innate immune- and sympathoadrenal- systems, which exerts a major long-term effect on glucose homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
High-fat diet induces periodontitis in mice through lipopolysaccharides (LPS) receptor signaling: protective action of estrogens.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048220. Epub 2012 Nov 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23133617 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of the cardiovascular and metabolic complications of obesity in CD14 knockout mice.Life Sci. 2008 Sep 26;83(13-14):502-10. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.07.021. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18761356
-
Changes in adiponectin and inflammatory genes in response to hormonal imbalances in female mice and exacerbation of depot selective visceral adiposity by high-fat diet: implications for insulin resistance.Endocrinology. 2007 Dec;148(12):5667-79. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0647. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17717050
-
Induction of TNF-alpha and MnSOD by endotoxin: role of membrane CD14 and Toll-like receptor-4.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001 Jun;280(6):C1422-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.280.6.C1422. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11350737
-
Acute low-dose endotoxin treatment results in improved whole-body glucose homeostasis in mice.Metabolism. 2017 Mar;68:150-162. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 16. Metabolism. 2017. PMID: 28183447 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD40 deficiency in mice exacerbates obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013 May 1;304(9):E951-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00514.2012. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23482447 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow lympho-myeloid malfunction in obesity requires precursor cell-autonomous TLR4.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 16;9(1):708. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03145-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29453396 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD14 in human disease.Immunology. 2023 Jul;169(3):260-270. doi: 10.1111/imm.13634. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Immunology. 2023. PMID: 36840585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-1 signaling in obesity-induced hepatic lipogenesis and steatosis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 12;9(9):e107265. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107265. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25216251 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble CD14 and Incident Diabetes Risk: The REasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) Study.J Endocr Soc. 2024 May 23;8(7):bvae097. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvae097. eCollection 2024 May 23. J Endocr Soc. 2024. PMID: 38817635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurt-Jones EA, Popova L, Kwinn L, Haynes LM, Jones LP, et al. Pattern recognition receptors TLR4 and CD14 mediate response to respiratory syncytial virus. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:398–401. - PubMed
-
- Faure E, Equils O, Sieling PA, Thomas L, Zhang FX, et al. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide activates NF-kappaB through toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) in cultured human dermal endothelial cells. Differential expression of TLR-4 and TLR-2 in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:11058–11063. - PubMed
-
- Nicola JP, Velez ML, Lucero AM, Fozzatti L, Pellizas CG, et al. Functional toll-like receptor 4 conferring lipopolysaccharide responsiveness is expressed in thyroid cells. Endocrinology. 2009;150:500–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

