Dietary phospholipids and intestinal cholesterol absorption
- PMID: 22254012
- PMCID: PMC3257636
- DOI: 10.3390/nu2020116
Dietary phospholipids and intestinal cholesterol absorption
Abstract
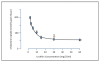
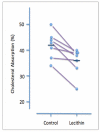
Experiments carried out with cultured cells and in experimental animals have consistently shown that phospholipids (PLs) can inhibit intestinal cholesterol absorption. Limited evidence from clinical studies suggests that dietary PL supplementation has a similar effect in man. A number of biological mechanisms have been proposed in order to explain how PL in the gut lumen is able to affect cholesterol uptake by the gut mucosa. Further research is however required to establish whether the ability of PLs to inhibit cholesterol absorption is of therapeutic benefit.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; cholesterol; intestine; micelle; phosphatidylcholine; phosphatidylethanolamine; phospholipid; sphingomyelin.
Figures
References
-
- Brugts J.J., Yetgin T., Hoeks S.E., Gotto A.M., Shepherd J., Westendorp R.G., de Craen A.J., Knopp R.H., Nakamura H., Ridker P., van Domburg R., Deckers J.W. The benefits of statins in people without established cardiovascular disease but with cardiovascular risk factors: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2009;338:b2376. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pandor A., Ara R.M., Tumur I., Wilkinson A.J., Paisley S., Duenas A., Durrington P.N., Chilcott J. Ezetimibe monotherapy for cholesterol lowering in 2,722 people: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Intern. Med. 2009;265:568–580. - PubMed
-
- Mikhailidis D.P., Sibbring G.C., Ballantyne C.M., Davies G.M., Catapano A.L. Meta-analysis of the cholesterol-lowering effect of ezetimibe added to ongoing statin therapy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2007;23:2009–2026. - PubMed
-
- Carr T.P., Jesch E.D. Food components that reduce cholesterol absorption. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2006;51:165–204. - PubMed
-
- Weihrauch J.L., Son Y.S. The phospholipid content of foods. JAOCS. 1983;60:1971–1978.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

