Mapping small intestine bioelectrical activity using high-resolution printed-circuit-board electrodes
- PMID: 22255449
- PMCID: PMC4076342
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6091227
Mapping small intestine bioelectrical activity using high-resolution printed-circuit-board electrodes
Abstract
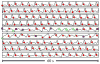
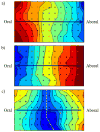
In this study, novel methods were developed for the in-vivo high-resolution recording and analysis of small intestine bioelectrical activity, using flexible printed-circuit-board (PCB) electrode arrays. Up to 256 simultaneous recordings were made at multiple locations along the porcine small intestine. Data analysis was automated through the application and tuning of the Falling-Edge Variable-Threshold algorithm, achieving 92% sensitivity and a 94% positive-predictive value. Slow wave propagation patterns were visualized through the automated generation of animations and isochronal maps. The methods developed and validated in this study are applicable for use in humans, where future studies will serve to improve the clinical understanding of small intestine motility in health and disease.
Figures

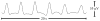
References
-
- Huizinga JD, Lammers WJ. Gut peristalsis is governed by a multitude of cooperating mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;296(1):G1–8. - PubMed
-
- Seidel SA, Hegde SS, Bradshaw LA, Ladipo JK, Richards WO. Intestinal tachydysrhythmias during small bowel ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:G993–9. - PubMed
-
- You CH, Chey WY, Lee KY, Menguy R, Bortoff A. Gastric and small intestinal myoelectric dysrhythmia associated with chronic intractable nausea and vomiting. Ann Intern Med. 1981;95:449–451. - PubMed
-
- Morrison P, Miedema BW, Kohler L, Kelly KA. Electrical dysrhythmias in the Roux jejunal limb: cause and treatment. Am J Surg. 1990;160:252–256. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez W, Mahoney L. Action currents in stomach and intestine. Am J Physiol. 1922;58(3):476–493.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
