An inexpensive alternative bath system for electrophysiological characterization of isolated cardiac tissue
- PMID: 22256302
- PMCID: PMC3513394
- DOI: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6092078
An inexpensive alternative bath system for electrophysiological characterization of isolated cardiac tissue
Abstract
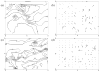
A tissue bath system, to be used as an alternative to complex perfusion chambers, was constructed for use in cardiac electrophysiological studies. This system consists of an acrylic chamber to hold circulating physiological medium such as DMEM, suspended in a water bath warmed by a hot plate. Temperature and pH were controlled to mimic physiological conditions. Rat and porcine cardiac tissues, were used to test viability of the conditions presented in the bath system. Using a cardiac mapping system, the tissues were stimulated and responses recorded. From the recordings we were able to calculate conduction velocities and spatial dispersion of activation indices. The results are comparable to previous in-vivo work, which suggests that the tissue bath system design can maintain tissue viability. This tissue bath system is a relatively simple alternative for ex-vivo testing of cardiac tissues.
Figures

References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010 Feb;121(7):e46–e215. - PubMed
-
- Prósper Cardoso F, Herreros González J, Alegría Ezquerra E. Stem cells to regenerate cardiac tissue in heart failure. Revista Española De Cardiología. 2003 Oct;56(10):935–939. - PubMed
-
- Bursac N, et al. Cardiac muscle tissue engineering: toward an in vitro model for electrophysiological studies. The American Journal of Physiology. 1999 Aug;277(2 Pt 2):H433–444. - PubMed
-
- Tormos A, et al. New epicardial mapping electrode with warming/cooling function for experimental electrophysiology studies. Medical Engineering & Physics. 2011 Jan; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
