Synthesis and secretion of renin in mice with induced genetic mutations
- PMID: 22258323
- PMCID: PMC3482822
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.451
Synthesis and secretion of renin in mice with induced genetic mutations
Abstract
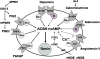
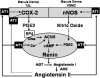
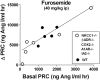
The juxtaglomerular (JG) cell product renin is rate limiting in the generation of the bioactive octapeptide angiotensin II. Rates of synthesis and secretion of the aspartyl protease renin by JG cells are controlled by multiple afferent and efferent pathways originating in the CNS, cardiovascular system, and kidneys, and making critical contributions to the maintenance of extracellular fluid volume and arterial blood pressure. Since both excesses and deficits of angiotensin II have deleterious effects, it is not surprising that control of renin is secured by a complex system of feedforward and feedback relationships. Mice with genetic alterations have contributed to a better understanding of the networks controlling renin synthesis and secretion. Essential input for the setting of basal renin generation rates is provided by β-adrenergic receptors acting through cyclic adenosine monophosphate, the primary intracellular activation mechanism for renin mRNA generation. Other major control mechanisms include COX-2 and nNOS affecting renin through PGE2, PGI2, and nitric oxide. Angiotensin II provides strong negative feedback inhibition of renin synthesis, largely an indirect effect mediated by baroreceptor and macula densa inputs. Adenosine appears to be a dominant factor in the inhibitory arms of the baroreceptor and macula densa mechanisms. Targeted gene mutations have also shed light on a number of novel aspects related to renin processing and the regulation of renin synthesis and secretion.
Figures
References
-
- Paul M, Poyan Mehr A, Kreutz R. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:747–803. - PubMed
-
- Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, et al. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59:251–287. - PubMed
-
- Pan L, Gross KW. Transcriptional regulation of renin: an update. Hypertension. 2005;45:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Todorov VT, Desch M, Schmitt-Nilson N, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is involved in the control of renin gene expression. Hypertension. 2007;50:939–944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

