Inhibition of p38 MAPK activity promotes ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 22258328
- PMCID: PMC3390192
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-011-1397-7
Inhibition of p38 MAPK activity promotes ex vivo expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
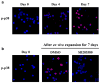
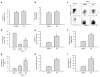
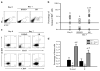
Ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) depends on HSC self-renewing proliferation and functional maintenance, which can be negatively affected by HSC differentiation, apoptosis, and senescence. Therefore, inhibition of HSC senescence may promote HSC expansion. To test this hypothesis, we examined the effect of inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) on the expansion of human umbilical cord blood (hUCB) CD133(+) cells because activation of p38 has been implicated in the induction of HSC senescence under various physiological and pathological conditions. Our results showed that ex vivo expansion of hUCB CD133(+) cells activated p38, which was abrogated by the p38 specific inhibitor SB203580 (SB). Inhibition of p38 activity with SB promoted the expansion of CD133(+) cells and CD133(+)CD38(-) cells. In addition, hUCB CD133(+) cells expanded in the presence of SB for 7 days showed about threefold increase in the clonogenic function of HSCs and engraftment in non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient mice after transplantation compared to the input cells. In contrast, the cells expanded without SB exhibited a significant reduction in these HSC functions. The enhancement of ex vivo expansion of hUCB HSCs is primarily attributable to SB-mediated inhibition of HSC senescence. In addition, inhibition of HSC apoptosis and upregulation of CXCR4 may also contribute to the enhancement. However, p38 inhibition had no significant effect on HSC differentiation and proliferation. These findings suggest that inhibition of p38 activation may represent a novel strategy to promote ex vivo expansion of hUCB HSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
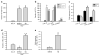
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase promotes ex vivo hematopoietic stem cell expansion.Stem Cells Dev. 2011 Jul;20(7):1143-52. doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0413. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Stem Cells Dev. 2011. PMID: 21198398 Free PMC article.
-
Coinhibition of activated p38 MAPKα and mTORC1 potentiates stemness maintenance of HSCs from SR1-expanded human cord blood CD34+ cells via inhibition of senescence.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020 Dec;9(12):1604-1616. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0129. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32602209 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin enhances long-term hematopoietic reconstitution of ex vivo expanded mouse hematopoietic stem cells by inhibiting senescence.Transplantation. 2014 Jan 15;97(1):20-9. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182a7fcf8. Transplantation. 2014. PMID: 24092377 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in umbilical cord blood stem cell expansion and clinical translation.Exp Hematol. 2015 Jul;43(7):498-513. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2015.04.011. Epub 2015 May 10. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25970610 Review.
-
Ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood stem cells for transplantation: growing knowledge from the hematopoietic niche.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007 Jan;39(1):11-23. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705538. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17164824 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclic AMP Signaling through Epac Axis Modulates Human Hemogenic Endothelium and Enhances Hematopoietic Cell Generation.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 May 10;6(5):692-703. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.03.006. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27117782 Free PMC article.
-
Development and clinical advancement of small molecules for ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cell.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jun;12(6):2808-2831. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.12.006. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35755294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ex Vivo Expansion and Homing of Human Cord Blood Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1442:85-104. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-7471-9_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 38228960
-
From causes of aging to death from COVID-19.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 12;12(11):10004-10021. doi: 10.18632/aging.103493. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32534452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates haematopoietic stem cell ageing and rejuvenation by inhibiting p38 kinase activity.Nat Commun. 2016 Dec 8;7:13674. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13674. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27929088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gluckman E, Rocha V, Arcese W, Michel G, Sanz G, Chan KW, Takahashi TA, Ortega J, Filipovich A, Locatelli F, Asano S, Fagioli F, Vowels M, Sirvent A, Laporte JP, Tiedemann K, Amadori S, Abecassis M, Bordigoni P, Diez B, Shaw PJ, Vora A, Caniglia M, Garnier F, Ionescu I, Garcia J, Koegler G, Rebulla P, Chevret S. Factors associated with outcomes of unrelated cord blood transplant: guidelines for donor choice. Exp Hematol. 2004;32:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Shpall EJ, Quinones R, Giller R, Zeng C, Baron AE, Jones RB, Bearman SI, Nieto Y, Freed B, Madinger N, Hogan CJ, Slat-Vasquez V, Russell P, Blunk B, Schissel D, Hild E, Malcolm J, Ward W, McNiece IK. Transplantation of ex vivo expanded cord blood. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002;8:368–376. - PubMed
-
- Peffault DLR, Purtill D, Ruggeri A, Sanz G, Michel G, Gandemer V, Maury S, Kurtzberg J, Bonfim C, Aljurf M, Gluckman E, Socie G, Passweg J, Rocha V. Influence of nucleated cell dose on overall survival of unrelated cord blood transplantation for patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia: a study by Eurocord and the Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17:78–85. - PubMed
-
- Devine SM, Lazarus HM, Emerson SG. Clinical application of hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion: current status and future prospects. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;31:241–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

