Central Pressure and Biomarker Responses to Renin Inhibition with Hydrochlorothiazide and Ramipril in Obese Hypertensives: The ATTAIN Study
- PMID: 22258466
- PMCID: PMC3101521
- DOI: 10.1159/000322864
Central Pressure and Biomarker Responses to Renin Inhibition with Hydrochlorothiazide and Ramipril in Obese Hypertensives: The ATTAIN Study
Abstract
Background/aims: In obese, hypertensive subjects, the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is enhanced and natriuresis impaired, suggesting a role for combination RAS blockade with diuretics. Data suggest that renin inhibition may attenuate diuretic-induced RAS activation and oxidative stress.
Methods: In this 8-week, double-blind study of 386 obese individuals (mean body mass index: 35.3) with stage 2 hypertension (mean age: 54.9 years; mean sitting systolic blood pressure, SBP: ≧160 but <200 mm Hg), we compared the efficacy of aliskiren + hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) in reducing blood pressure (BP), plasma renin activity (PRA), and a urinary marker of oxidative stress to ramipril. Subjects were randomized to aliskiren/HCTZ 150/12.5 mg or ramipril 5 mg for 1 week, and after the 1st week force titrated to aliskiren/HCTZ 300/25 mg or ramipril 10 mg for 7 weeks.
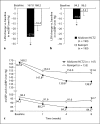
Results: After 8 weeks, aliskiren/HCTZ provided greater reductions in office BP than ramipril (-28.1/-10.1 vs. -16.6/-3.6 mm Hg, p < 0.0001) as well as 24-hour ambulatory and central pressure measures. Aliskiren/HCTZ also lowered PRA (-45 vs. +83%) and the urinary F2-isoprostane/creatinine ratio (-18 vs. +7%) to a greater extent than ramipril. Adverse events (AEs) were similar in the two groups (35.8% with aliskiren/HCTZ vs. 37.3% on ramipril reporting at least one AE).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that the aliskiren/HCTZ combination reduced BP, PRA, and isoprostanes to a greater extent than did ramipril in obese patients with stage 2 hypertension.
Keywords: Aliskiren; Hydrochlorothiazide; Obesity; Plasma renin activity; Ramipril; Stage 2 hypertension.
© 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Long-term safety and tolerability of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren with optional add-on hydrochlorothiazide in patients with hypertension: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, dose-escalation study with an extension phase.Clin Drug Investig. 2011 Dec 1;31(12):825-37. doi: 10.1007/BF03256921. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 22035463 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative effects of aliskiren-based and ramipril-based therapy on the renin system during long-term (6 months) treatment and withdrawal in patients with hypertension.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2009 Sep;10(3):157-67. doi: 10.1177/1470320309342407. Epub 2009 Jul 17. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2009. PMID: 19617271 Clinical Trial.
-
Lack of pharmacokinetic interactions of aliskiren, a novel direct renin inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension, with the antihypertensives amlodipine, valsartan, hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) and ramipril in healthy volunteers.Int J Clin Pract. 2006 Nov;60(11):1343-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01164.x. Int J Clin Pract. 2006. PMID: 17073832
-
Aliskiren: a review of its use as monotherapy and as combination therapy in the management of hypertension.Drugs. 2010 Oct 22;70(15):2011-49. doi: 10.2165/11204360-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20883056 Review.
-
Aliskiren: a review of its use in the management of hypertension.Drugs. 2007;67(12):1767-92. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767120-00008. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17683174 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology and management of hypertension in the Hispanic population: a review of the available literature.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012 Jun 1;12(3):165-78. doi: 10.2165/11631520-000000000-00000. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22583147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aliskiren alone or in combination with hydrochlorothiazide in Hispanic/Latino patients with systolic blood pressure 160 mm Hg to <180 mm Hg (Aliskiren Alone or in Combination with Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients with Stage 2 Hypertension to Provide Quick Intensive Control of Blood Pressure [ACQUIRE] substudy).J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2012 Aug;14(8):514-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00672.x. Epub 2012 Jun 7. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2012. PMID: 22863159 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Aliskiren/amlodipine as a single-pill combination in hypertensive patients: subgroup analysis of elderly patients, with metabolic risk factors or high body mass index.J Drug Assess. 2012 Dec 25;2(1):1-10. doi: 10.3109/21556660.2012.762367. eCollection 2013. J Drug Assess. 2012. PMID: 27536431 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aliskiren- and ramipril-based treatment on central aortic blood pressure in elderly with systolic hypertension: a substudy of AGELESS.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014 Jun 25;10:389-97. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S63725. eCollection 2014. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014. PMID: 25061313 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, Eckel RH, American Heart Association, Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss: an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on Obesity and Heart Disease from the Obesity Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation. 2006;113:898–918. - PubMed
-
- Bramlage P, Pittrow D, Wittchen HU, Kirch W, Boehler S, Lehnert H, Hoefler M, Unger T, Sharma AM. Hypertension in overweight and obese primary care patients is highly prevalent and poorly controlled. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:904–910. - PubMed
-
- Esler M, Straznicky N, Eikelis N, Masuo K, Lambert G, Lambert E. Mechanisms of sympathetic activation in obesity-related hypertension. Hypertension. 2006;48:787–796. - PubMed
-
- Hall JE. The kidney, hypertension, and obesity. Hypertension. 2003;41:625–633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
