Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin
- PMID: 22258959
- PMCID: PMC11984800
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005060.pub3
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin
Abstract
Background: Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) has been found to be effective for patients with type 1 diabetes and for patients with type 2 diabetes using insulin. There is much debate on the effectiveness of SMBG as a tool in the self-management for patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin.
Objectives: To assess the effects of SMBG in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin.
Search methods: Multiple electronic bibliographic and ongoing trial databases were searched supplemented with handsearches of references of retrieved articles (date of last search: 07 July 2011).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials investigating the effects of SMBG compared with usual care, self-monitoring of urine glucose (SMUG) or both in patients with type 2 diabetes who where not using insulin. Studies that used glycosylated haemoglobin A(1c) (HbA(1c)) as primary outcome were eligible for inclusion.
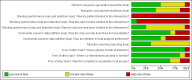
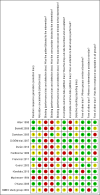
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data from included studies and evaluated the studies' risk of bias. Data from the studies were compared to decide whether they were sufficiently homogeneous to pool in a meta-analysis. Primary outcomes were HbA(1c), health-related quality of life, well-being and patient satisfaction. Secondary outcomes were fasting plasma glucose level, hypoglycaemic episodes, morbidity, adverse effects and costs.
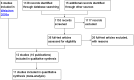
Main results: Twelve randomised controlled trials were included and evaluated outcomes in 3259 randomised patients. Intervention duration ranged from 6 months (26 weeks) to 12 months (52 weeks). Nine trials compared SMBG with usual care without monitoring, one study compared SMBG with SMUG, one study was a three-armed trial comparing SMBG and SMUG with usual care and one study was a three-armed trial comparing less intensive SMBG and more intensive SMBG with a control group. Seven out of 11 studies had a low risk of bias for most indicators. Meta-analysis of studies including patients with a diabetes duration of one year or more showed a statistically significant SMBG induced decrease in HbA(1c) at up to six months follow-up (-0.3; 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.4 to -0.1; 2324 participants, nine trials), yet an overall statistically non-significant SMBG induced decrease was seen at 12 month follow-up (-0.1; 95% CI -0.3 to 0.04; 493 participants, two trials). Qualitative analysis of the effect of SMBG on well-being and quality of life showed no effect on patient satisfaction, general well-being or general health-related quality of life. Two trials reported costs of self-monitoring: One trial compared the costs of self-monitoring of blood glucose with self-monitoring of urine glucose based on nine measurements per week and with the prices in US dollars for self-monitoring in 1990. Authors concluded that total costs in the first year of self-monitoring of blood glucose, with the purchase of a reflectance meter were 12 times more expensive than self-monitoring of urine glucose ($481 or 361 EURO [11/2011 conversion] versus $40 or 30 EURO [11/2011 conversion]). Another trial reported a full economical evaluation of the costs and effects of self-monitoring. At the end of the trial, costs for the intervention were £89 (104 EURO [11/2011 conversion]) for standardized usual care (control group), £181 (212 EURO [11/2011 conversion]) for the less intensive self-monitoring group and £173 (203 EURO [11/2011 conversion]) for the more intensive self-monitoring group. Higher losses to follow-up in the more intensive self-monitoring group were responsible for the difference in costs, compared to the less intensive self-monitoring group.There were few data on the effects on other outcomes and these effects were not statistically significant. None of the studies reported data on morbidity.
Authors' conclusions: From this review, we conclude that when diabetes duration is over one year, the overall effect of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin is small up to six months after initiation and subsides after 12 months. Furthermore, based on a best-evidence synthesis, there is no evidence that SMBG affects patient satisfaction, general well-being or general health-related quality of life. More research is needed to explore the psychological impact of SMBG and its impact on diabetes specific quality of life and well-being, as well as the impact of SMBG on hypoglycaemia and diabetic complications.
Conflict of interest statement
URIËLL MALANDA, JACQUELINE DEKKER, GIEL NIJPELS and SANDRA BOT all take part in an ongoing study on the topic of interest of this review.
Figures


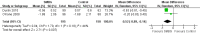





Update of
-
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD005060. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005060.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD005060. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005060.pub3. PMID: 15846742 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Allen 1990 {published data only}
-
- Allen BT, DeLong ER, Feussner JR. Impact of glucose self‐monitoring on non‐insulin‐treated patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Randomized controlled trial comparing blood and urine testing. Diabetes Care 1990;13(10):1044‐50. - PubMed
Barnett 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barnett AH, Krentz AJ, Strojek K, Sieradzki J, Azizi F, Embong M, et al. The efficacy of self‐monitoring of blood glucose in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with a gliclazide modified release‐based regimen. A multicentre, randomized, parallel‐group, 6‐month evaluation (DINAMIC 1 study). Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.10(12)()(pp 1239‐1247), 2008.Date of Publication: 2008. 2008;10(12):1239‐47. - PubMed
Davidson 2005 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Davidson MB, Castellanos M, Kain D, Duran P. The effect of self‐monitoring of blood glucose concentrations on glycated hemoglobin levels in diabetic patients not taking insulin: a blinded, randomized trial.. American Journal of Medicine 04‐2005;118(4):422‐25. - PubMed
DiGEM trial 2007 {published data only}
-
- Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al. Blood glucose self‐monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment. 2009;13(15):iii‐xi, 1. - PubMed
-
- French DP, Wade AN, Yudkin P, Neil HAW, Kinmonth AL, Farmer AJ. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose changed non‐insulin‐treated Type 2 diabetes patients' beliefs about diabetes and self‐monitoring in a randomized trial. Diabetic Medicine.25(10)()(pp 1218‐1228), 2008.Date of Publication: October 2008. 2008;25(10):1218‐28. - PubMed
Durán 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Durán A, Martín P, Runkle I, Pérez N, Abad R, Fernández M, Valle L, Sanz MF, Calle‐Pascual L. Benefits of self‐monitoring blood glucose in the management of new‐onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus: The St Carlos Study, a prospective randomized clinic‐based interventional study with parallel groups. Journal of Diabetes 2010;2:203‐211. - PubMed
Fontbonne 1989 {published data only}
-
- Fontbonne A, Billault B, Acosta M, Percheron C, Varenne P, Besse A, et al. Is glucose self‐monitoring beneficial in non‐insulin‐treated diabetic patients? Results of a randomized comparative trial. Diabete & Metabolisme 1989;15(5):255‐60. - PubMed
Franciosi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Franciosi M, Lucisano G, Pellegrini F, Cantarello A, Consoli A, Cucco L, et al. ROSES: role of self‐monitoring of blood glucose and intensive education in patients with Type 2 diabetes not receiving insulin. A pilot randomized clinical trial. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association 2011;28(7):789‐96. [PUBMED: 21342243] - PubMed
Guerci 2003 {published data only}
-
- Guerci B, Drouin P, Grange V, Bougneres P, Fontaine P, Kerlan V, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose significantly improves metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Auto‐Surveillance Intervention Active (ASIA) study. Diabetes Metab 2003;29(6):587‐94. - PubMed
Kleefstra 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kleefstra N, Hortensius J, Logtenberg SJJ, Slingerland RJ, Groenier KH, Houweling ST, Gans ROB, Ballegooie E, Bilo HJG. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in tablet‐treated type 2 diabetic patients (ZODIAC). Neth.J.Med. ‐08‐2010;68(1):311‐316. - PubMed
Muchmore 1994 {published data only}
-
- Muchmore DB, Springer J, Miller M. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in overweight type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol 1994;31(4):215‐9. - PubMed
O'Kane 2008 {published data only}
SMBG study group 2002 {published data only}
-
- Schwedes U, Siebolds M, Mertes G. Meal‐related structured self‐monitoring of blood glucose: effect on diabetes control in non‐insulin‐treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002;25(11):1928‐32. - PubMed
-
- Siebolds M, Gaedeke O, Schwedes U, SMBG Study Group. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose‐‐psychological aspects relevant to changes in HbA1c in type 2 diabetic patients treated with diet or diet plus oral antidiabetic medication. Patient education and counseling. 2006;62(1):104‐10. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdelgadir 2006 {published data only}
-
- Abdelgadir M, Elbagir M, Eltom M, Berne C. The influence of glucose self‐monitoring on glycaemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus in Sudan. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.74(1)()(pp 90‐94), 2006.Date of Publication: Oct 2006. 2006;74(1):90‐4. - PubMed
Atsumi 1997 {published data only}
-
- Atsumi Y, Kadowaki Y, Origasa H. Self‐monitoring blood glucose improves quality of life in NIDDM patients treated with diet alone or oral hypo‐glycaemic agents. Diabetes 1997; Vol. 46 (Suppl 1):267A.
Bajkowska‐Fiedziukiewicz 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bajkowska‐Fiedziukiewicz A, Cypryk K, Kozdraj T, Mikolajczyk‐Swatko A, Kosinski M, Jozefowska M. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose and treatment outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients. Polskie Archiwum Medycyny Wewnetrznej.118(5):267‐72, 2008;118(5):267‐72. - PubMed
Chidum 2011 {published data only}
-
- Chidum E, Agbai D, Fidelis O, Teppany S, Martina R, Rian E, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose improved glycaemic control and 10‐year coronary heart disease risk profile of type 2 diabetic patients. Chinese medical journal 2011;124(2):166‐71. [PUBMED: 21362359] - PubMed
Cho 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cho JH, Chang SA, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Ko SH, Moon SD, et al. Long‐term effect of the Internet‐based glucose monitoring system on HbA1c reduction and glucose stability: a 30‐month follow‐up study for diabetes management with a ubiquitous medical care system. Diabetes care 2006;29(12):2625‐31. [PUBMED: 17130195] - PubMed
Davidson 2004 {published data only}
-
- Davidson Mayer B, Castellanos Maria, Kain Don. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) linked to nutritional counseling in minority type 2 diabetic patients on diet and oral antidiabetes medication does not improve glycemic outcomes. Diabetes 2004; Vol. 53 (Suppl):A73.
Drouin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Drouin P, Grange V, Bougneres P, Fontaine P, Kerlan V, Passa P, et al. An impact of self‐monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) on metabolic control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2002; Vol. 45 (Suppl 20):A310.
Franciosi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Franciosi M, Pellegrini F, Berardis G, Belfiglio M, Nardo B, Greenfield S, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in non‐insulin‐treated diabetic patients: A longitudinal evaluation of its impact on metabolic control. Diabetic Medicine.22(7)()(pp 900‐906), 2005.Date of Publication: Jul 2005. 2005;22(7):900‐6. - PubMed
Gallego 2007 {published data only}
Hoffmann 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hoffmann F, Andersohn F. Immortal time bias and survival in patients who self‐monitor blood glucose in the Retrolective Study: self‐monitoring of Blood Glucose and Outcome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (ROSSO). Diabetologia 2011;54(2):308‐11. [PUBMED: 20853097] - PubMed
Johnson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Johnson JA, Majumdar SR, Bowker SL, Toth EL, Edwards A. Self‐monitoring in Type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial of reimbursement policy. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association. 2006;23(11):1247‐51. - PubMed
Kelly 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kelly KL, Ellison JM, Goldstein E, Nomura DM, Price DA. Self‐monitoring in Type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial of reimbursement policy. Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association 2007; Vol. 24, issue 7:802. [PUBMED: 17596241] - PubMed
Kwon 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kwon HS, Cho JH, Kim HS, Song BR, Ko SH, Lee JM, et al. Establishment of blood glucose monitoring system using the internet. Diabetes Care 2004;27(2):478‐83. - PubMed
Laffel 2007 {published data only}
-
- Laffel LM Hsu WC McGill JB Meneghini. Continued use of an integrated meter with electronic logbook maintains improvements in glycemic control beyond a randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes technology & therapeutics 2007;9(3):254‐64. - PubMed
Lecomte 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lecomte P, Romon I, Fosse S, Simon D, Fagot‐Campagna A. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes living in France: The Entred study 2001. Diabetes and Metabolism.34(3)()(pp 219‐226), 2008.Date of Publication: June 2008. 2008;34(3):219‐26. - PubMed
Lim 2011 {published data only}
Mohan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mohan V, Ravikumar R, Poongothai S, Amutha A, Sowmya S, Karkhuzali K, et al. A single‐center, open, comparative study of the effect of using self‐monitoring of blood glucose to guide therapy on preclinical atherosclerotic markers in type 2 diabetic subjects. Journal of diabetes science and technology 2010;4(4):942‐8. [PUBMED: 20663460] - PMC - PubMed
Moreland 2006 {published data only}
-
- Moreland EC, Volkening LK, Lawlor MT, Chalmers KA, Anderson BJ, Laffel LM. Use of a blood glucose monitoring manual to enhance monitoring adherence in adults with diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166(6):689‐95. - PubMed
O'Kane 2006 {published data only}
-
- O'Kane MJ, Coates VE, Bunting B. The efficacy of self blood glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes: the ESMON study. Diabetologia 2006; Vol. 49 (Suppl 1):550.
Pignone 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pignone M. Value of self‐monitoring of blood glucose in non‐insulin‐using patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Diabetes.27(1)()(pp 17‐18), 2009.Date of Publication: January 2009. 2009;27(1):17‐8.
Polonsky 2011 {published data only}
-
- Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Schikman CH, Hinnen DA, Parkin CG, Jelsovsky Z, et al. Structured self‐monitoring of blood glucose significantly reduces A1C levels in poorly controlled, noninsulin‐treated type 2 diabetes: results from the Structured Testing Program study. Diabetes care 2011;34(2):262‐7. [PUBMED: 21270183] - PMC - PubMed
Scherbaum 2008 {published data only}
Shiraiwa 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shiraiwa T, Takahara M, Kaneto H, Miyatsuka T, Yamamoto K, Yoshiuchi K, et al. Efficacy of occasional self‐monitoring of postprandial blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetic patients without insulin therapy. Diabetes research and clinical practice 2010; Vol. 90, issue 3:e91‐2. [PUBMED: 21030103] - PubMed
Tengblad 2007 {published data only}
Wen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wen L, Parchman ML, Linn WD, Lee S. Association between self‐monitoring of blood glucose and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. American journal of health system pharmacy : AJHP : official journal of the American Society of Health System Pharmacists. 2004;61(22):2401‐5. - PubMed
Wysocki 1989 {published data only}
-
- Wysocki Tim. Impact of blood glucose monitoring on diabetic control: Obstacles and interventions. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 1989;12(2):183‐205. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Bergenstal 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Impact of Self‐Monitoring Blood Glucose Frequency on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Ongoing study September 2004.
Additional references
ADA 1999
-
- The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1999;22(Suppl 1):S5‐19. - PubMed
ADA 2008
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes ‐ 2008. Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl 1):S12‐54. [PUBMED: 18165335] - PubMed
ADA 2010
Allemann 2009
-
- Allemann S, Houriet C, Diem P, Stettler C. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in non‐insulin treated patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2009;25(1473‐4877 (Electronic), 0300‐7995 (Linking), 12):2903‐13. - PubMed
Bode 1999
-
- Bode BW, Gross TM, Thornton KR, Mastrototaro JJ. Continuous glucose monitoring used to adjust diabetes therapy improves glycosylated hemoglobin: a pilot study. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 1999;46(3):183‐90. - PubMed
Bradley 1994a
-
- Bradley C. The Well‐Being Questionnaire. In: Bradley C editor(s). Handbook of Psychology and Diabetes: A Guide to Psychological Measurement in Diabetes Research and Practice. Chur, Switzerland: Harwood Academic, 1994:89‐109.
Bradley 1994b
-
- Bradley C. Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire. In: Bradley C editor(s). Handbook of psychology and diabetes: A guide to psychological measurement in diabetes research and practice. Chur: Harwood Academic, 1994:111‐32.
Clar 2010
-
- Clar C, Barnard K, Cummins E, Royle P, Waugh N. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: systematic review. Health Technology Assessment Reports 2010;14(1366‐5278 (Print), 1366‐5278 (Linking), 12):1‐140. - PubMed
Cohen 1960
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1960;20:37‐46.
Davidson 2005a
-
- Davidson MB. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: response to Welschen et al. and Kleefstra et al. Diabetes Care 2005;28(0149‐5992 (Print), 0149‐5992 (Linking), 10):2597‐8. - PubMed
Davidson 2010
-
- Davidson MB. Evaluation of Self Monitoring of Blood Glucose in Non‐Insulin‐Treated Diabetic Patients by Randomized Controlled Trials: Little Bang for the Buck. Rev Recent Clin Trials 2010;‐(1876‐1038 (Electronic)):‐. - PubMed
DCCT 1993
-
- DCCT group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(14):977‐86. - PubMed
Farmer 2005
-
- Farmer A, Wade A, French DP, Goyder E, Kinmonth AL, Neil A. The DiGEM trial protocol‐‐a randomised controlled trial to determine the effect on glycaemic control of different strategies of blood glucose self‐monitoring in people with type 2 diabetes [ISRCTN47464659]. BMC Family Practice 2005;6(1471‐2296 (Electronic)):25. - PMC - PubMed
Farmer 2007
Farmer 2009
-
- Farmer AJ, Wade AN, French DP, Simon J, Yudkin P, Gray A, et al. Blood glucose self‐monitoring in type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment 2009;13(15):iii‐xi, 1. - PubMed
French 2008
-
- French DP, Wade AN, Yudkin P, Neil HAW, Kinmonth AL, Farmer AJ. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose changed non‐insulin‐treated Type 2 diabetes patients' beliefs about diabetes and self‐monitoring in a randomized trial. Diabetic Medicine 2008;25(10):1218‐28. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009.
Jansen 2006
-
- Jansen JP. Self‐monitoring of glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Bayesian meta‐analysis of direct and indirect comparisons. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(0300‐7995 (Print), 4):671‐81. - PubMed
Karter 2001
-
- Karter AJ, Ackerson LM, Darbinian JA, D'Agostino RB Jr, Ferrara A, Liu J, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose levels and glycemic control: the Northern California Kaiser Permanente Diabetes registry. The American Journal of Medicine 2001;111(0002‐9343 (Print), 1):1‐9. - PubMed
Kempf 2008
-
- Kempf K, Neukirchen W, Martin S, Kolb H. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in type 2 diabetes: a new look at published trials. Diabetologia 2008;51(0012‐186X (Print), 4):686‐8. - PubMed
Kleefstra 2005
-
- Kleefstra N, Houweling ST, Ballegooie E, Bilo HJ. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: response to Welschen et al. Diabetes Care 2005;28(0149‐5992 (Print), 0149‐5992 (Linking), 10):2596‐8. - PubMed
Kleefstra 2009
Klonoff 2008
Kolb 2010
-
- Kolb H, Kempf K, Martin S, Stumvoll M, Landgraf R. On what evidence‐base do we recommend self‐monitoring of blood glucose?. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2010;87(1872‐8227 (Electronic), 0168‐8227 (Linking), 2):150‐6. - PubMed
Lau 2006
Leventhal 1980
-
- Leventhal H, Meyer D, Nerenz D. The common sense representation of illness danger. In: Rachman S editor(s). Contributions to medical psychology. Vol. 2, New York: Pergamon Press, 1980:17‐30.
Leventhal 1997
-
- Leventhal L, Benyamini Y, Brownlee S, Diefenbach M, Leventhal EL, Patrick‐Miller L, et al. Illness representations: theoretical foundations. In: Petrie, K.J, Weinman, J editor(s). Perceptions of health and illness. Amsterdam: Harwood Academic Publisher, 1997:19.
Liberati 2009
-
- Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta‐analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009;339(1468‐5833 (Electronic), 0959‐535X (Linking)):b2700. - PMC - PubMed
McAndrew 2007
-
- McAndrew L, Schneider SH, Burns E, Leventhal H. Does patient blood glucose monitoring improve diabetes control? A systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Educator 2007;33(0145‐7217 (Print), 0145‐7217 (Linking), 6):991‐1011. - PubMed
McGeoch 2007
-
- McGeoch G, Derry S, Moore RA. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in type‐2 diabetes: what is the evidence?. Diabetes/metabolism Research and Reviews 2007;23(1520‐7552 (Print), 6):423‐40. - PubMed
McIntosh 2010
Nathan 1996
-
- Nathan DM, Mckitrick C, Larkin M, Schaffran R, Singer DE. Glycemic control in diabetes mellitus: have changes in therapy made a difference?. The American Journal of Medicine 1996;100(2):157‐63. - PubMed
O'Kane 2009
-
- O'Kane MJ, Pickup J. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in diabetes: is it worth it?. AACN Clinical Issues 2009;46(1758‐1001 (Electronic), 0004‐5632 (Linking), Pt 4):273‐82. - PubMed
Olivarius 2001
Peel 2007
Piatt 2006
-
- Piatt GA, Orchard TJ, Emerson S, Simmons D, Songer TJ, Brooks MM, et al. Translating the chronic care model into the community: results from a randomized controlled trial of a multifaceted diabetes care intervention. Diabetes Care 2006;29(0149‐5992 (Print), 4):811‐7. - PubMed
Poolsup 2008
-
- Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Jiamsathit W. Systematic review of the benefits of self‐monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2008;10(SUPPL. 1):S51‐66. - PubMed
Poolsup 2009
-
- Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Rattanasookchit S. Meta‐analysis of the benefits of self‐monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: an update. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2009;11(1557‐8593 (Electronic), 1520‐9156 (Linking), 12):775‐84. - PubMed
Rothman 2005
-
- Rothman RL, Malone R, Bryant B, Shintani AK, Crigler B, DeWalt DA, et al. A randomized trial of a primary care‐based disease management program to improve cardiovascular risk factors and glycated hemoglobin levels in patients with diabetes. American Journal of Medicine 2005;118(0002‐9343 (Print), 3):276‐84. - PubMed
Sarol 2005
-
- Sarol JN Jr, Nicodemus NA Jr, Tan KM, Grava MB. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose as part of a multi‐component therapy among non‐insulin requiring type 2 diabetes patients: a meta‐analysis (1966‐2004). Current Medical Research and Opinion 2005;21(0300‐7995 (Print), 2):173‐84. - PubMed
Schwedes 2002
-
- Schwedes Ulrich, Siebolds Markus, Mertes Gabriele. Meal‐related structured self‐monitoring of blood glucose: effect on diabetes control in non‐insulin‐treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002;25(11):1928‐32. - PubMed
Siebolds 2006
-
- Siebolds M, Gaedeke O, Schwedes U, SMBG Study Group. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose‐‐psychological aspects relevant to changes in HbA1c in type 2 diabetic patients treated with diet or diet plus oral antidiabetic medication. Patient education and Counseling 2006;62(1):104‐10. - PubMed
Simon 2008
St John 2010
-
- John A, Davis WA, Price CP, Davis TM. The value of self‐monitoring of blood glucose: a review of recent evidence. Journal of Diabetic Complications 2010;24(1873‐460X (Electronic), 1056‐8727 (Linking), 2):129‐41. - PubMed
Sterne 2001
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Davey Smith G. Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care; Meta‐analysis in Context. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2001:189‐208.
Towfigh 2008
-
- Towfigh A, Romanova M, Weinreb JE, Munjas B, Suttorp MJ, Zhou A, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not taking insulin: a meta‐analysis. American Journal of Managed Care 2008;14(1936‐2692 (Electronic), 7):468‐75. - PubMed
Wagner 2001
-
- Wagner EH, Grothaus LC, Sandhu N, Galvin MS, McGregor M, Artz K, et al. Chronic care clinics for diabetes in primary care: a system‐wide randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2001;24(0149‐5992 (Print), 4):695‐700. - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐item short‐form health survey (SF‐36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med.Care 1992;30(0025‐7079 (Print), 0025‐7079 (Linking), 6):473‐83. - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- Alberti KM, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part I: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15:539‐53. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Welschen 2005a
-
- Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Stalman WA, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin. Cochrane Database.Syst.Rev. 2005;issue 2(1469‐493X, 2):CD005060. - PubMed
Welschen 2005b
-
- Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, Heine RJ, Stalman WA, et al. Self‐monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: a systematic review. Diabetes Care 2005;28(0149‐5992, 6):1510‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

