Continuous glucose monitoring systems for type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 22258980
- PMCID: PMC6486112
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008101.pub2
Continuous glucose monitoring systems for type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Self-monitoring of blood glucose is essential to optimise glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems measure interstitial fluid glucose levels to provide semi-continuous information about glucose levels, which identifies fluctuations that would not have been identified with conventional self-monitoring. Two types of CGM systems can be defined: retrospective systems and real-time systems. Real-time systems continuously provide the actual glucose concentration on a display. Currently, the use of CGM is not common practice and its reimbursement status is a point of debate in many countries.
Objectives: To assess the effects of CGM systems compared to conventional self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1.
Search methods: We searched The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL for the identification of studies. Last search date was June 8, 2011.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing retrospective or real-time CGM with conventional self-monitoring of blood glucose levels or with another type of CGM system in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Primary outcomes were glycaemic control, e.g. level of glycosylated haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and health-related quality of life. Secondary outcomes were adverse events and complications, CGM derived glycaemic control, death and costs.
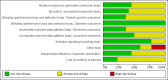
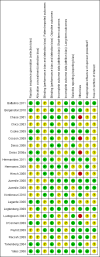
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected the studies, assessed the risk of bias and performed data-extraction. Although there was clinical and methodological heterogeneity between studies an exploratory meta-analysis was performed on those outcomes the authors felt could be pooled without losing clinical merit.
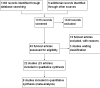
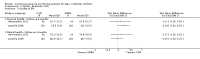
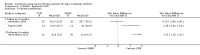
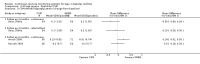
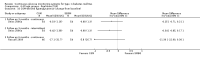
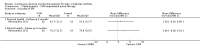
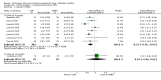
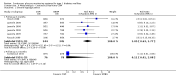
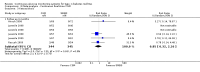
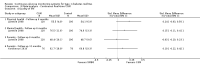
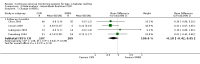
Main results: The search identified 1366 references. Twenty-two RCTs meeting the inclusion criteria of this review were identified. The results of the meta-analyses (across all age groups) indicate benefit of CGM for patients starting on CGM sensor augmented insulin pump therapy compared to patients using multiple daily injections of insulin (MDI) and standard monitoring blood glucose (SMBG). After six months there was a significant larger decline in HbA1c level for real-time CGM users starting insulin pump therapy compared to patients using MDI and SMBG (mean difference (MD) in change in HbA1c level -0.7%, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.8% to -0.5%, 2 RCTs, 562 patients, I(2)=84%). The risk of hypoglycaemia was increased for CGM users, but CIs were wide and included unity (4/43 versus 1/35; RR 3.26, 95% CI 0.38 to 27.82 and 21/247 versus 17/248; RR 1.24, 95% CI 0.67 to 2.29). One study reported the occurrence of ketoacidosis from baseline to six months; there was however only one event. Both RCTs were in patients with poorly controlled diabetes.For patients starting with CGM only, the average decline in HbA1c level six months after baseline was also statistically significantly larger for CGM users compared to SMBG users, but much smaller than for patients starting using an insulin pump and CGM at the same time (MD change in HbA1c level -0.2%, 95% CI -0.4% to -0.1%, 6 RCTs, 963 patients, I(2)=55%). On average, there was no significant difference in risk of severe hypoglycaemia or ketoacidosis between CGM and SMBG users. The confidence interval however, was wide and included a decreased as well as an increased risk for CGM users compared to the control group (severe hypoglycaemia: 36/411 versus 33/407; RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.62, 4 RCTs, I(2)=0% and ketoacidosis: 8/411 versus 8/407; RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.36 to 2.40, 4 RCTs, I(2)=0%).Health-related quality of life was reported in five of the 22 studies. In none of these studies a significant difference between CGM and SMBG was found. Diabetes complications, death and costs were not measured.There were no studies in pregnant women with diabetes type 1 and in patients with hypoglycaemia unawareness.
Authors' conclusions: There is limited evidence for the effectiveness of real-time continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use in children, adults and patients with poorly controlled diabetes. The largest improvements in glycaemic control were seen for sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy in patients with poorly controlled diabetes who had not used an insulin pump before. The risk of severe hypoglycaemia or ketoacidosis was not significantly increased for CGM users, but as these events occurred infrequent these results have to be interpreted cautiously.There are indications that higher compliance of wearing the CGM device improves glycosylated haemoglobin A1c level (HbA1c) to a larger extent.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Hans DeVries is co‐author of the Hermanides trial (Hermanides 2011).
Other authors: none known.
Figures


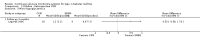
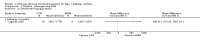

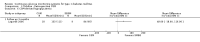
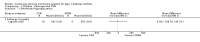





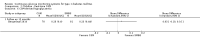
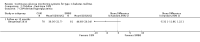






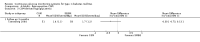
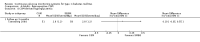




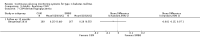

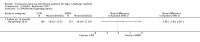
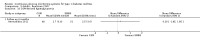





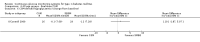


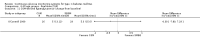
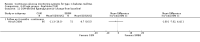
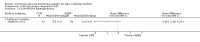





Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Battelino 2011 {published data only}
Bergenstal 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bergenstal RM, Tamborlane WV, Ahmann A, Buse JB, Dailey G, Davis SN, et al. Effectiveness of Sensor‐Augmented Insulin‐Pump Therapyin Type 1 Diabetes. British Medical Journal 2010;363(4):311‐20. - PubMed
Chase 2001 {published data only}
-
- Chase HP, Kim LM, Owen SL, MacKenzie TA, Klingensmith G, Murtfeldt R, et al. Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatrics 2001;107(2):222‐6. - PubMed
Chico 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chico A, Vidal‐Rios P, Subira M, Novials A. The continuous glucose monitoring system is useful for detecting unrecognized hypoglycemias in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes but is not better than frequent capillary glucose measurements for improving metabolic control. Diabetes Care 2003;4:1153‐7. - PubMed
Cooke 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cooke D, Hurel SJ, Casbard A, Steed L, Walker S, Meredith A, et al. Randomized controlled trial to assess the impact ofcontinuous glucose monitoring on HbA1c in insulintreateddiabetes (MITRE Study). Diabetic Medicine 2009;26:540‐547. - PubMed
Cosson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cosson E, Hamo‐Tchatchouang E, Dufaitre‐Patouraux L, Attali J‐R, Paris J, Schaepelynck BP. Multicentre, randomised, controlled study of the impact of continuous sub‐cutaneous glucose monitoring (GlucoDay) on glycaemic control in type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes & Metabolism 2009;35:312‐8. - PubMed
Deiss 2006 {published data only}
-
- Deiss D, Hartmann R, Schmidt J, Kordonouri O. Results of a randomised controlled cross‐over trial on the effect of continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring (CGMS) on glycaemic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes 2006;2:63‐7. - PubMed
Deiss 2006a {published data only}
-
- Deiss D, Bolinder J, Riveline JP, Battelino T, Bosi E, Tubiana‐Rufi N, et al. Improved glycemic control in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes using real‐time continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2006;29(12):2730‐2. - PubMed
Hermanides 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hermanides J, Norgaard K, Bruttomesso D, Mathieu C, Frid A, Dayan CM, Diem P, Vermon C, Wentholt I, DeVries JH. Sensor‐augmented pump therapy lowers HbA1c in suboptimally controlled type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial.. Diabetic Medicine 2011;28(10):1158‐67. - PubMed
Hermanns 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hermanns N, Kulzer B, Gulde C, Eberle H, Pradler E, Patzelt‐Bath A, et al. Short‐term effects on patient satisfaction of continuous glucose monitoring with the glucoday with real‐time and retrospective access to glucose values: A crossover study. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2009;5:275‐81. - PubMed
Hirsch 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hirsch IB, Abelseth J, Bode BW, Fischer JS, Kaufman FR, Mastrototaro J, et al. Sensor‐augmented insulin pump therapy: Results of the first randomized treat‐to‐target study. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2008;5:377‐83. - PubMed
Juvenile 2008 {published data only}
-
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group, Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;359(14):1464‐76. - PubMed
Juvenile 2009 {published data only}
Kordonouri 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kordonouri O, Pankowska E, Rami B, Kapellen T, Coutant R, Hartmann R, et al. Sensor‐augmented pump therapy from the diagnosis of childhood type 1 diabetes: results of the Pediatric Onset Study (ONSET) after 12 months of treatment. Diabetologia 2010;53(12):2487‐95. - PubMed
Lagarde 2006 {published data only}
-
- Lagarde WH, Barrows FP, Davenport ML, Kang M, Guess HA, Calikoglu AS. Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A single‐blind, randomized, controlled trial. Pediatric Diabetes 2006;3:159‐64. - PubMed
Logtenberg 2009 {published data only}
-
- Logtenberg SJJ, Kleefstra N, Groenier KH, Gans ROB, Bilo HJG. Use of short‐term real‐time continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes patients on continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion: A feasibility study. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2009;5:293‐9. - PubMed
Ludvigsson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ludvigsson J, Hanas R. Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring improved metabolic control in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes: A controlled crossover study. Pediatrics 2003;5:933‐8. - PubMed
O'Connell 2009 {published data only}
-
- O'Connell MA, Donath D, O'Neal DN, Colman P, Ambler GR, Jones TW, et al. Glycaemic impact of patient‐led use of sensor‐guided pump therapy in type 1 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2009;52:1250‐7. - PubMed
Peyrot 2009 {published data only}
-
- Peyrot M, Rubin RR. Patient‐reported outcomes for an integrated real‐time continuous glucose monitoring/insulin pump system. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2009;11(1):57‐62. - PubMed
Raccah 2009 {published data only}
Tanenberg 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tanenberg R, Bode B, Lane W, Levetan C, Mestman J, Harmel AP, et al. Use of the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System to guide therapy in patients with insulin‐treated diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2004;79(12):1521‐6. - PubMed
Yates 2006 {published data only}
-
- Yates K, Milton AH, Dear K, Ambler G. Continuous glucose monitoring‐guided insulin adjustment in children and adolescents on near‐physiological insulin regimens: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2006;7:1512‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bode 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bode B, Gross K, Rikalo N, Schwartz S, Wahl T, Page C, et al. Alarms Based on Real‐Time Sensor Glucose Values Alert Patients to Hypo‐ and Hyperglycemia: The Guardian Continuous Monitoring System. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2004;2:105‐13. - PubMed
Bode 2004a {published data only}
-
- Bode B, Shelmet J, Gooch B, Hassman DR, Liang J, Smedegaard JK, et al. Patient perception and use of an insulin injector/glucose monitor combined device. Diabetes Educator 2004;30(2):301‐9. - PubMed
Chase 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chase HP, Roberts MD, Wightman C, Klingensmith G, Garg SK, Wyhe M, et al. Use of the GlucoWatch biographer in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatrics 2003;4:790‐4. - PubMed
Chase 2005 {published data only}
-
- Chase HP. A randomized multicenter trial comparing the glucowatch biographer with standard glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005;5:1101‐6. - PubMed
Feldman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Feldman B, Brazg R, Schwartz S, Weinstein R. A Continuous Glucose Sensor Based on Wired Enzyme[trademark] Technology ‐ Results from a 3‐Day Trial in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2003;5:769‐79. - PubMed
Fiallo‐Scharer 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fiallo‐Scharer R. Eight‐point glucose testing Versus the continuous glucose monitoring system in evaluation of glycemic control in type 1 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2005;6:3387‐91. - PubMed
Garg 2006 {published data only}
-
- Garg S, Zisser H, Schwartz S, Bailey T, Kaplan R, Ellis S, et al. Improvement in glycemic excursions with a transcutaneous, real‐time continuous glucose sensor: A randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2006;1:44‐50. - PubMed
Garg 2008 {published data only}
Haupt 2005 {published data only}
-
- Haupt A, Berg B, Paschen P, Dreyer M, Haring HU, Smedegaard J, et al. InDuo, a novel combined insulin injection and blood glucose monitoring device ‐ effective and save as other devices, and patient preference. Experimental & Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes 2005;113(9):541‐4. - PubMed
Jeha 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jeha GS, Karaviti LP, Anderson B, Smith EO'B, Donaldson S, Mcgirk TS, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and the reality of metabolic control in preschool children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004;12:2881‐6. - PubMed
Juvenile 2009a {published data only}
Murphy 2008 {published data only}
Rowen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rowen M, Schneider DJ, Pratley RE, Sobel BE. On rendering continuous glucose monitoring ready for prime time in the cardiac care unit. Coronary Artery Disease 2007;18(5):405‐9. - PubMed
Tamborlane 2008 {published data only}
-
- Tamborlane WV, Ruedy KJ, Wysocki T, O'Grady M, Kollman C, Block J, et al. JDRF randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy of real‐time continuous glucose monitoring in the management of type 1 diabetes: Research design and methods. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2008;4:310‐21. - PubMed
Weinzimer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Weinzimer S, Xing D, Tansey M, Fiallo‐Scharer R, Mauras N, Wysocki T, et al. FreeStyle navigator continuous glucose monitoring system use in children with type 1 diabetes using glargine‐based multiple daily dose regimens: Results of a pilot trial diabetes research in children network (DirecNet) study group. Diabetes Care 2008;3:525‐7. - PMC - PubMed
Wilhelm 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wilhelm B, Forst S, Weber MM, Larbig M, Pfutzner A, Forst T. Evaluation of CGMS during rapid blood glucose changes in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2006;2:146‐55. - PubMed
Wysocki 2005 {published data only}
Yogev 2003 {published data only}
-
- Yogev Y, Ben‐Haroush A, Chen R, Kaplan B, Phillip M, Hod M. Continuous glucose monitoring for treatment adjustment in diabetic pregnancies ‐ A pilot study. Diabetic Medicine 2003;7:558‐62. - PubMed
Yogev 2003a {published data only}
-
- Yogev Y, Chen R, Ben‐Haroush A, Phillip M, Jovanovic L, Hod M. Continuous glucose monitoring for the evaluation of gravid women with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;4:633‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Conget 2010 {published data only}
-
- Conget I, Battelino T, Gimenez M, Gough H, Castaseda J, Bolinder J. The SWITCH study (Sensing with insulin pump therapy to control HbA1c). Design and methods of a randomized controlled cross‐over trial on sensor‐augmented insulin pump efficacy in type 1 diabetes sub‐optimally controlled with pump therapy. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2011;13(1):49‐54. - PubMed
Lange 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lange K, Coutant R, Danne T, Kapellen T, Pankowska, Rami B, Aschemeier B, Blsig S, Hartmann R, Krug N, Marquardt E, Remus K, Kordonouri O. High quality of life in children and psychological wellbeing in mothers 12 months after diabetes onset: results of the paediatric onset‐trial of sensor‐enhanced CSII. Pediatric Diabetes 2010;11(Suppl s14):101.
Langeland 2010 {published data only}
-
- Langeland LL, Salvesen O, Selle H, Carlsen SM, Fougner KJ. Continuous glucose monitoring: effect on glucose control and treatment satisfaction in diabetes mellitus type 1. Diabetologica 2010;53(Supplement 1):S423. - PubMed
Additional references
ADA 1999
-
- The Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the Expert Committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1999;22 Suppl 1:S5‐19. - PubMed
Boland 2001
-
- Boland E, Monsod T, Delucia M, Brandt CA, Fernando S, Tamborlane WV. Limitations of conventional methods of self‐monitoring of blood glucose: lessons learned from 3 days of continuous glucose sensing in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24:1858‐62. - PubMed
Bradburn 2007
-
- Bradburn MJ, Deeks JJ, Berlin JA, Russell LA. Much ado about nothing: a comparison of the performance of meta‐analytical methods with rare events. Statistics in Medicine 2007;26:53‐77. - PubMed
Bradley 1994a
-
- Bradley C. The Well‐being Questionnaire. In: Bradley C editor(s). Handbook of Psychology and Diabetes: a guide to psychological measurement in diabetes research and practice. Harwood Academic Publishers, 1994:89‐109.
Bradley 1994b
-
- Bradley C. Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire (DTSQ). In: Bradley C editor(s). Handbook of Psychology and Diabetes. Harwood Academic Publishers, 1994:111‐32.
Brauker 2009
-
- Brauker J. Continuous glucose sensing: future technology developments. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2009;11(s1):s25‐s36. - PubMed
Chetty 2008
-
- Chetty VT, Almulla A, Odueyungbo A, Thabane L. The effect of continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring (CGMS) versus intermittent whole blood finger‐stick glucose monitoring (SBGM) on hemoglobin A1c (HBA1c) levels in Type I diabetic patients: a systematic review. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2008;81:79‐87. - PubMed
Cohen 1960
-
- Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1960;20:37‐46.
Cryer 2004
-
- Cryer PE. Diverse causes of hypoglycaemia‐associated autonomic failure in diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;350:2272‐9. - PubMed
DCCT 1993
-
- DCCT Research Group. The diabetes control and complications trial research group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long‐term complications in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(14):977‐86. - PubMed
FDA 2009
-
- US Food, Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry. Diabetes Mellitus: developing drugs and therapeutic biologics for treatment and prevention (Draft guidance). US Food and Drug Administration 2009.
Ghandi 2011
-
- Ghandi GY, Kovalaske M, Kudva Y, Walsh K, Elamin MB, Beers M, Coyle C, Goalen M, Safwan Murad M, Erwin PJ, Corpus J, Montori VM, Murad MH. Efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in improving glycaemic control and reducing hypoglycemia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology 2011;5(4):952‐965. - PMC - PubMed
Girardin 2009
-
- Girardin CM, Huot C, Gonthier M, Delvin E. Continuous glucose monitoring: a review of biochemical perspectives and clinical use in type 1 diabetes. Clinical Biochemistry 2009;42:136‐142. - PubMed
Golicki 2008
-
- Golicki DT, Golicka D, Groele L, Pankowska E. Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetologica 2008;51:233‐40. - PubMed
Grootenhuis 1994
-
- Grootenhuis PA, Snoek FJ, Heine RJ, Bouter LM. Development of a type 2 diabetes symptom checklist: a measure of symptom severity. Diabetic Medicine 1994;11(3):253‐61. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.0 [updated February 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hoeks 2010
-
- Hoeks LBEA, Greven WL, Valk HW. Review Article: Real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system fortreatment of diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetic Medicine 2010;doi: 10.1111/j.1464‐5491.2010.03177.x:In press. - PubMed
Klonoff 2005
-
- Klonoff DC. Continuous glucose monitoring. Roadmap for 21st century diabetes therapy. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1231‐9. - PubMed
Lau 2006
Liberati 2009
McHorney 1993
-
- McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Raczek AE. The MOS 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey (SF‐36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs.. Medical Care 1993;31(3):247‐63. - PubMed
Nathan 2005
NCCWCH 1994
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Women's and Children's Health. Type 1 diabetes diagnosis and management of type 1 diabetes in children and young people. London: RCOG Press, 2004. - PubMed
Pickup 2011
RevMan 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). 5.0 for Windows. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Sterne 2001
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Davey Smith G. Investigating and dealing with publication and other biases. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Health Care; Meta‐analysis in Context. London: BMJ Publishing Group, 2001:189‐208.
Thierny 2000
-
- Thierney MJ, Tamada JA, Potts RO, Eastman RC, Pitzer K, Ackerman NR, Fermi SJ. The GlucoWatch Biographer: a frequent, automatic and noninvasive glucose monitor. Annals in Medicine 2000;32:641. - PubMed
Wentholt 2005
-
- Wentholt IM, Vollebregt MA, Hart AA, Hoekstra JB, Vries JH. Comparison of a needle‐type and a microdialysis continuous glucose monitor in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2005;28(12):2871‐6. - PubMed
Wentholt 2007
-
- Wentholt IME, Hoekstra JBL, Vries JH. Continuous glucose monitors: the long awaited watch dogs?. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2007;9(5):399‐409. - PubMed
Wentholt 2008
-
- Wentholt IM, Hart AA, Hoekstra JB, Vries JH. How to assess and compare the accuracy of continuous glucose monitors?. Diabetes Technol Ther 2008;10(2):57‐68. - PubMed
WHO 1980
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus. Second report. Technical Report Series 646. Geneva. WHO, 1980. - PubMed
WHO 1985
-
- WHO Expert Committee on Diabetes Mellitus. World Health Organization, 1985. Technical Report Series 727. - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- Alberti KM, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its compliactions. Part I: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15:539‐53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

