Differential effects of delta and epsilon protein kinase C in modulation of postischemic cerebral blood flow
- PMID: 22259083
- PMCID: PMC4086166
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-1566-4_10
Differential effects of delta and epsilon protein kinase C in modulation of postischemic cerebral blood flow
Abstract
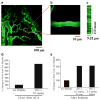
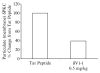
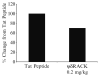
Cerebral ischemia causes cerebral blood flow (CBF) derangements resulting in neuronal damage by enhanced protein kinase C delta (δPKC) levels leading to hippocampal and cortical neuronal death after ischemia. Contrarily, activation of εPKC mediates ischemic tolerance by decreasing vascular tone providing neuroprotection. However, whether part of this protection is due to the role of differential isozymes of PKCs on CBF following cerebral ischemia remains poorly understood. Rats pretreated with a δPKC specific inhibitor (δV1-1, 0.5 mg/kg) exhibited attenuation of hyperemia and latent hypoperfusion characterized by vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation of microvessels after two-vessel occlusion plus hypotension. In an asphyxial cardiac arrest (ACA) model, rats treated with δ V1-1 (pre- and postischemia) exhibited improved perfusion after 24 h and less hippocampal CA1 and cortical neuronal death 7 days after ACA. On the contrary, εPKC-selective peptide activator, conferred neuroprotection in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus 30 min before induction of global cerebral ischemia and decreased regional CBF during the reperfusion phase. These opposing effects of δ v. εPKC suggest a possible therapeutic potential by modulating CBF preventing neuronal damage after cerebral ischemia.
Figures
References
-
- Hossmann KA. Reperfusion of the brain after global ischemia: hemodynamic disturbances. Shock. 1997;8:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK. Interrupting reperfusion as a stroke therapy: ischemic postconditioning reduces infarct size after focal ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:1114–1121. - PubMed
-
- Caplan LR, Wong KS, Gao S, Hennerici MG. Is hypoperfusion an important cause of strokes? If so, how? Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006;21:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Raval AP, Dave KR, Prado R, et al. Protein kinase C delta cleavage initiates an aberrant signal transduction pathway after cardiac arrest and oxygen glucose deprivation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:730–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

