Molecular detection of Campylobacter jejuni as a cause of culture-negative spondylodiscitis
- PMID: 22259199
- PMCID: PMC3318547
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.06275-11
Molecular detection of Campylobacter jejuni as a cause of culture-negative spondylodiscitis
Abstract
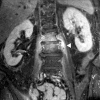
Spondylodiscitis caused by Campylobacter species is a rare disease which is most often caused by Campylobacter fetus. We report a case of culture-negative spondylodiscitis and a psoas abscess due to Campylobacter jejuni in a 68-year-old woman, as revealed by 16S rRNA gene and Campylobacter-specific PCRs from biopsied tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus spondylodiscitis.J Med Microbiol. 2010 Dec;59(Pt 12):1505-1508. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.023382-0. Epub 2010 Aug 12. J Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20705728
-
Campylobacter jejuni, an uncommon cause of splenic abscess diagnosed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing.Int J Infect Dis. 2014 Dec;29:238-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Int J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25447730
-
Speciating Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolates from poultry and humans using six PCR-based assays.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002 Nov 5;216(2):201-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11436.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002. PMID: 12435503
-
[Campylobacter fetus spondylodiscitis].Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1992 Jan;59(1):77-9. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1992. PMID: 1579850 Review. French.
-
[Simple and rapid detection methods for campylobacters].Nihon Rinsho. 2012 Aug;70(8):1305-12. Nihon Rinsho. 2012. PMID: 22894063 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Vertebral osteomyelitis with Campylobacter jejuni - a case report and review of the literature of a very rare disease.J Bone Jt Infect. 2024 Feb 12;9(1):59-65. doi: 10.5194/jbji-9-59-2024. eCollection 2024. J Bone Jt Infect. 2024. PMID: 38601004 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter fetus-induced primary psoas abscess in patient with gouty arthritis: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 22;102(51):e36333. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036333. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38134096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Campylobacter fetus caused pyogenic spondylodiscitis with a presentation of cauda equina syndrome after instrumented lumbar fusion surgery.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 4;9:998011. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.998011. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36268208 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual case of infective spondylodiscitis caused by Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus: molecular characterization by whole-genome sequencing.Access Microbiol. 2021 Jul 8;3(7):000240. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000240. eCollection 2021. Access Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34595392 Free PMC article.
-
Vertebral osteomyelitis caused by Campylobacter jejuni in an immunocompetent patient.Gut Pathog. 2023 Nov 30;15(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13099-023-00589-2. Gut Pathog. 2023. PMID: 38037181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachmeyer C, Grateau G, Sereni D, Cremer GA. 1992. Campylobacter fetus spondylodiscitis. Rev. Rhum. Mal. Osteoartic. 59:77–79 (In French.) - PubMed
-
- Bundesinstitut für Riskobewertung 2010. Wissenschaftliche Bewertung der Ergebnisse des Resistenzmonitorings nach dem Zoonosen-Stichprobenplan 2009. Stellungnahme Nr. 047/2010 des BfR, vom 1, November 2010. (In German.)
-
- Chaillon A, et al. 2010. Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus spondylodiscitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 59:1505–1508 - PubMed
-
- Denis M, et al. 1999. Development of a m-PCR assay for simultaneous identification of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 29:406–410 - PubMed
-
- Feodoroff B, Lauhio A, Ellström P, Rautelin H. 2011. A nationwide study of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli bacteremia in Finland over a 10-year period, 1998-2007, with special reference to clinical characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 53:e99–e106 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

